Quantitative expression analysis and prognostic significance of the BCL2-associated X gene in nasopharyngeal carcinoma: a retrospective cohort study
- PMID: 23777485
- PMCID: PMC3689087
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2407-13-293
Quantitative expression analysis and prognostic significance of the BCL2-associated X gene in nasopharyngeal carcinoma: a retrospective cohort study
Abstract
Background: Nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) is a highly metastatic epithelial malignancy showing high prevalence in Southeast Asia and North Africa. The BCL2-associated X (BAX) gene encodes the most important pro-apoptotic member of the BCL2 family. We have recently shown that BCL2 and BCL2L12, two other members of the same apoptosis-related family, possess significant prognostic value in NPC. The objective of the current study was to analyze BAX mRNA expression in nasopharyngeal biopsies of NPC patients, and to assess its prognostic potential in this disease.
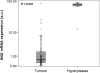
Methods: Total RNA was isolated from 88 malignant and 9 hyperplastic nasopharyngeal biopsies, resected from Tunisian patients. After cDNA synthesis by reverse transcription of polyadenylated RNA, BAX mRNA expression was analyzed using a highly sensitive quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) method.
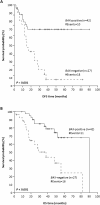
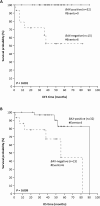
Results: Lower BAX mRNA levels were detected in NPC biopsies than in hyperplastic nasopharyngeal samples. BAX mRNA expression status was associated with low tumor extent, negative regional lymph node status, and absence of distant metastases. Kaplan-Meier survival analysis demonstrated that patients with BAX mRNA-positive NPC have significantly longer disease-free survival (DFS) and overall survival (OS). In accordance with these findings, Cox regression analysis revealed that BAX mRNA expression can be considered as a favorable prognostic indicator of DFS and OS in NPC, independent of their gender, age, tumor histology, tumor extent, and nodal status. Furthermore, NPC patients without distant metastases are less likely to relapse when their primary tumor is BAX mRNA-positive, compared to metastasis-free patients with a BAX-negative nasopharyngeal malignancy.
Conclusion: This is the first study examining the potential clinical utility of BAX as a prognostic tumor biomarker in NPC. We provide evidence that BAX mRNA expression can be considered as an independent favorable prognostic indicator of DFS and OS in NPC.
Figures
References
-
- Reed JC. Dysregulation of apoptosis in cancer. J Clin Oncol. 1999;17(9):2941–2953. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

