Early resuscitation intensity as a surrogate for bleeding severity and early mortality in the PROMMTT study
- PMID: 23778506
- PMCID: PMC3744217
- DOI: 10.1097/TA.0b013e31828fa535
Early resuscitation intensity as a surrogate for bleeding severity and early mortality in the PROMMTT study
Abstract
Background: The classic definition of massive transfusion, 10 or more units of red blood cells (RBCs) in 24 hours, has never been demonstrated as a valid surrogate for severe hemorrhage and can introduce survival bias. In addition, the definition fails to capture other products that the clinician may have immediately available, and may use, during the initial resuscitation. Assuming that units of resuscitative fluids reflect patient illness, our objective was to identify a rate of resuscitation intensity (RI) that could serve as an early surrogate of sickness for patients with substantial bleeding after injury.
Methods: Adult patients surviving at least 30 minutes after admission and receiving one or more RBCs within 6 hours of admission from 10 US Level 1 trauma centers were enrolled in the PRospective Observational Multicenter Major Trauma Transfusion (PROMMTT) study. Total fluid units were calculated as the sum of the number of crystalloid units (1 L = 1 U), colloids (0.5 L = 1 U), and blood products (1 RBC = 1 U, 1 plasma = 1 U, 6 pack platelets = 1 U). Univariable and multivariable logistic regressions were used to evaluate associations between RI and 6-hour mortality, adjusting for age, center, penetrating injury, weighted Revised Trauma Score (RTS), and Injury Severity Score (ISS).
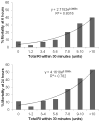
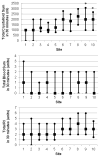
Results: A total of 1,096 eligible patients received resuscitative fluids within 30 minutes, including 620 transfused with blood products. Despite varying products used, the total fluid RI was similar across all sites (3.2 ± 2.5 U). Patients who received four or more units of any resuscitative fluid had a 6-hour mortality rate of 14.4% versus 4.5% in patients who received less than 4 U. The adjusted odds ratio of 6-hour mortality for patients receiving 4 U or more within 30 minutes was 2.1 (95% confidence interval, 1.2-3.5).
Conclusion: Resuscitation with four or more units of any fluid was significantly associated with 6-hour mortality. This study suggests that early RI regardless of fluid type can be used as a surrogate for sickness and mortality in severely bleeding patients.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Cothren CC, Moore EE, Hedegaard HB, Meng K. Epidemiology of urban trauma deaths: a comprehensive reassessment 10 years later. World J Surg. 2007;31:1507–1511. - PubMed
-
- Sauaia A, Moore FA, Moore EE, et al. Epidemiology of trauma deaths: a reassessment. J Trauma. 1995;38:185–193. - PubMed
-
- Kauvar DS, Lefering R, Wade CE. Impact of hemorrhage on trauma outcome: an overview of epidemiology, clinical presentations, and therapeutic considerations. J Trauma. 2006;60(6 suppl):S3–S11. - PubMed
-
- Demetriades D, Murray J, Charalambides K, et al. Trauma fatalities: time and location of hospital deaths. J Am Coll Surg. 2004;198:20–26. - PubMed
-
- Holcomb JB, Jenkins D, Rhee P, et al. Damage control resuscitation: directly addressing the early coagulopathy of trauma. J Trauma. 2007;62:307–310. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

