Commensal bacteria at the interface of host metabolism and the immune system
- PMID: 23778795
- PMCID: PMC4013146
- DOI: 10.1038/ni.2640
Commensal bacteria at the interface of host metabolism and the immune system
Abstract
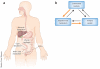
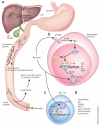
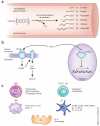
The mammalian gastrointestinal tract, the site of digestion and nutrient absorption, harbors trillions of beneficial commensal microbes from all three domains of life. Commensal bacteria, in particular, are key participants in the digestion of food, and are responsible for the extraction and synthesis of nutrients and other metabolites that are essential for the maintenance of mammalian health. Many of these nutrients and metabolites derived from commensal bacteria have been implicated in the development, homeostasis and function of the immune system, suggesting that commensal bacteria may influence host immunity via nutrient- and metabolite-dependent mechanisms. Here we review the current knowledge of how commensal bacteria regulate the production and bioavailability of immunomodulatory, diet-dependent nutrients and metabolites and discuss how these commensal bacteria-derived products may regulate the development and function of the mammalian immune system.
Figures
References
-
- Shin SC, et al. Drosophila microbiome modulates host developmental and metabolic homeostasis via insulin signaling. Science. 2011;334:670–674. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 AI074878/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32-AI060516/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI095466/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI061570/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI102942/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI074878/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI087990/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI060516/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI087990/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI095608/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI083480/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI095608/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI061570/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI097333/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI083480/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI102942/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI097333/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI095466/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

