ATP-sensitive potassium (K(ATP)) channel openers diazoxide and nicorandil lower intraocular pressure in vivo
- PMID: 23778875
- PMCID: PMC3720149
- DOI: 10.1167/iovs.13-11872
ATP-sensitive potassium (K(ATP)) channel openers diazoxide and nicorandil lower intraocular pressure in vivo
Abstract
Purpose: To evaluate the expression of ATP-sensitive potassium (K(ATP)) channel subunits and study the effect of K(ATP) channel openers diazoxide and nicorandil on intraocular pressure (IOP) in an in vivo mouse model.
Methods: Expression of K(ATP) channel subunits in normal C57BL/6 mouse eyes was studied by immunohistochemistry and confocal microscopy. Wild-type C57BL/6 mice were treated with K(ATP) channel openers diazoxide (n = 10) and nicorandil (n = 10) for 14 days. Similar treatments with diazoxide were performed on K(ir)6.2((-/-)) mice (n = 10). IOP was recorded with a handheld tonometer 1 hour, 4 hours, and 23 hours following daily treatment. Posttreatment histology was examined by light and transmission electron microscopy.
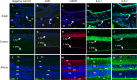
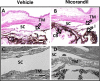
Results: The K(ATP) channel subunits SUR2B, K(ir)6.1, and K(ir)6.2 were identified in all tissues within mouse eyes. Treatment with diazoxide in wild-type mice decreased IOP by 21.5 ± 3.2% with an absolute IOP reduction of 3.9 ± 0.6 mm Hg (P = 0.002). Nicorandil also decreased IOP (18.9 ± 1.8%) with an absolute IOP reduction of 3.4 ± 0.4 mm Hg (P = 0.002). Treatment with diazoxide in K(ir)6.2((-/-)) mice had no effect on IOP. No morphological abnormalities were observed in diazoxide- or nicorandil-treated eyes.
Conclusions: K(ATP) channel openers diazoxide and nicorandil are effective regulators of IOP in mouse eyes. K(ir)6.2 appears to be a major K(ATP) channel subunit through which IOP is lowered following treatment with diazoxide.
Keywords: anterior segment; intraocular pressure; potassium channel.
Figures




Similar articles
-
ATP-sensitive potassium (KATP) channel activation decreases intraocular pressure in the anterior chamber of the eye.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011 Aug 16;52(9):6435-42. doi: 10.1167/iovs.11-7523. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011. PMID: 21743021 Free PMC article.
-
ATP-sensitive potassium (KATP) channel openers diazoxide and nicorandil lower intraocular pressure by activating the Erk1/2 signaling pathway.PLoS One. 2017 Jun 8;12(6):e0179345. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0179345. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28594895 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of ATP-sensitive Potassium Channel Openers on Intraocular Pressure in Ocular Hypertensive Animal Models.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2022 Feb 1;63(2):15. doi: 10.1167/iovs.63.2.15. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2022. PMID: 35129587 Free PMC article.
-
ATP sensitive potassium channel openers: A new class of ocular hypotensive agents.Exp Eye Res. 2017 May;158:85-93. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2016.04.020. Epub 2016 Apr 26. Exp Eye Res. 2017. PMID: 27130546 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ATP-sensitive K+ channel openers: old drugs with new clinical benefits for the heart.Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2003 Oct;1(3):251-8. doi: 10.2174/1570161033476646. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2003. PMID: 15320472 Review.
Cited by
-
Novel Therapeutics in Glaucoma Management.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2018;16(7):978-992. doi: 10.2174/1570159X15666170915142727. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2018. PMID: 28925883 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Subconjunctival Administration of an Adeno-Associated Virus Expressing Stanniocalcin-1 Provides Sustained Intraocular Pressure Reduction in Mice.Ophthalmol Sci. 2024 Jul 31;5(1):100590. doi: 10.1016/j.xops.2024.100590. eCollection 2025 Jan-Feb. Ophthalmol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39328825 Free PMC article.
-
Ocular Hypotensive Properties and Biochemical Profile of QLS-101, a Novel ATP-Sensitive Potassium (KATP) Channel Opening Prodrug.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2022 Apr 1;63(4):26. doi: 10.1167/iovs.63.4.26. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2022. PMID: 35486069 Free PMC article.
-
Analogs of the ATP-Sensitive Potassium (KATP) Channel Opener Cromakalim with in Vivo Ocular Hypotensive Activity.J Med Chem. 2016 Jul 14;59(13):6221-31. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.6b00406. Epub 2016 Jul 1. J Med Chem. 2016. PMID: 27367033 Free PMC article.
-
Ocular Hypotensive Effects of the ATP-Sensitive Potassium Channel Opener Cromakalim in Human and Murine Experimental Model Systems.PLoS One. 2015 Nov 4;10(11):e0141783. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0141783. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26535899 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Heijl A, Leske MC, Bengtsson B, Hyman L, Hussein M. Reduction of intraocular pressure and glaucoma progression: results from the Early Manifest Glaucoma Trial. Arch Ophthalmol. 2002; 120: 1268–1279 - PubMed
-
- Alm A, Grierson I, Shields MB. Side effects associated with prostaglandin analog therapy. Surv Ophthalmol. 2008; 53 (suppl 1): S93–S105 - PubMed
-
- Talluto DM, Wyse TB, Krupin T. Topical carbonic anhydrase inhibitors. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 1997; 8: 2–6 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

