Biological implications and regulatory mechanisms of long-range chromosomal interactions
- PMID: 23779110
- PMCID: PMC3829327
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.R113.485292
Biological implications and regulatory mechanisms of long-range chromosomal interactions
Abstract
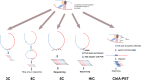
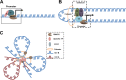
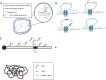
Development of high-throughput sequencing-based methods has enabled us to examine nuclear architecture at unprecedented resolution, allowing further examination of the function of long-range chromosomal interactions. Here, we review methods used to investigate novel long-range chromosomal interactions and genome-wide organization of chromatin. We further discuss transcriptional activation and silencing in relation to organization and positioning of gene loci and regulation of chromatin organization through protein complexes and noncoding RNAs.
Keywords: Chromatin; Chromatin Regulation; Chromatin Structure; Chromosome Conformation Capture; Nuclear Organization; Nuclear Structure.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Genome-Scale Imaging of the 3D Organization and Transcriptional Activity of Chromatin.Cell. 2020 Sep 17;182(6):1641-1659.e26. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.07.032. Epub 2020 Aug 20. Cell. 2020. PMID: 32822575 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamics and interplay of nuclear architecture, genome organization, and gene expression.Genes Dev. 2007 Dec 1;21(23):3027-43. doi: 10.1101/gad.1604607. Genes Dev. 2007. PMID: 18056419 Review.
-
Klf4 organizes long-range chromosomal interactions with the oct4 locus in reprogramming and pluripotency.Cell Stem Cell. 2013 Jul 3;13(1):36-47. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2013.05.010. Epub 2013 Jun 6. Cell Stem Cell. 2013. PMID: 23747203
-
Combined immunofluorescence, RNA fluorescent in situ hybridization, and DNA fluorescent in situ hybridization to study chromatin changes, transcriptional activity, nuclear organization, and X-chromosome inactivation.Methods Mol Biol. 2008;463:297-308. doi: 10.1007/978-1-59745-406-3_18. Methods Mol Biol. 2008. PMID: 18951174
-
Simulation of different three-dimensional polymer models of interphase chromosomes compared to experiments-an evaluation and review framework of the 3D genome organization.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2019 Jun;90:19-42. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2018.07.012. Epub 2018 Aug 24. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2019. PMID: 30125668 Review.
Cited by
-
Intronic variant of EGFR is associated with GBAS expression and survival outcome of early-stage non-small cell lung cancer.Thorac Cancer. 2018 Aug;9(8):916-923. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.12757. Epub 2018 May 28. Thorac Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29806744 Free PMC article.
-
lncRNA 5430416N02Rik Promotes the Proliferation of Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells by Activating Mid1 Expression through 3D Chromatin Architecture.Stem Cell Reports. 2020 Mar 10;14(3):493-505. doi: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2020.02.002. Stem Cell Reports. 2020. PMID: 32160522 Free PMC article.
-
Genome organization by Klf4 regulates transcription in pluripotent stem cells.Cell Cycle. 2013 Nov 1;12(21):3351-2. doi: 10.4161/cc.26577. Epub 2013 Sep 23. Cell Cycle. 2013. PMID: 24091533 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Identification of Gene Positioning Factors Using High-Throughput Imaging Mapping.Cell. 2015 Aug 13;162(4):911-23. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.07.035. Cell. 2015. PMID: 26276637 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying growth hormone-regulated enhancers in the Igf1 locus.Physiol Genomics. 2015 Nov;47(11):559-68. doi: 10.1152/physiolgenomics.00062.2015. Epub 2015 Sep 1. Physiol Genomics. 2015. PMID: 26330488 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cremer T., Cremer C. (2006) Rise, fall and resurrection of chromosome territories: a historical perspective. Part II. Fall and resurrection of chromosome territories during the 1950s to 1980s. Part III. Chromosome territories and the functional nuclear architecture: experiments and models from the 1990s to the present. Eur. J. Histochem. 50, 223–272 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

