Effects of naked gold nanoparticles on proinflammatory cytokines mRNA expression in rat liver and kidney
- PMID: 23781503
- PMCID: PMC3677657
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/590730
Effects of naked gold nanoparticles on proinflammatory cytokines mRNA expression in rat liver and kidney
Abstract
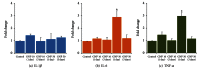
The data on the biocompatibility of naked gold nanoparticles (GNPs) are scarce, and their interpretation is controversial. We studied the acute (1 day) and subchronic (5 days) effects of GNPs (10 and 50 nm diameter) on expression of interleukin-1 beta (IL-1 β ), interleukin-6 (IL-6), and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF- α ) in the liver and kidneys of rats. In the liver, the GNPs of both sizes (10 and 50 nm) significantly increased the cytokines gene expression on day 1 which was subsided on day 5; the GNPs of 50 nm size produced more severe inflammatory response as compared to smaller sized GNPs. In the kidney, the GNPs did not produce any significant change in the expression of IL-1 β . Although the gene expression of IL-6 and TNF- α was not affected by GNPs of 10 nm size, 50 nm GNPs significantly increased the expression of IL-6 and TNF- α in the kidneys of rats on day 1 after treatment which returned to normalcy on day 5. These findings indicate the possible immunocompatibility of medium sized GNPs as they caused only a transient acute phase increase in proinflammatory cytokines expression followed by their normalcy during the repeated exposure.
Figures

References
-
- Pissuwan D, Niidome T, Cortie MB. The forthcoming applications of gold nanoparticles in drug and gene delivery systems. Journal of Controlled Release. 2011;149(1):65–71. - PubMed
-
- Craig GE, Brown SD, Lamprou DA, Graham D, Wheate NJ. Cisplatin-tethered gold nanoparticles that exhibit enhanced reproducibility, drug loading, and stability: a step closer to pharmaceutical approval? Inorganic Chemistry. 2012;51:3490–3497. - PubMed
-
- Tom RT, Suryanarayanan V, Reddy PG, Baskaran S, Pradeep T. Ciprofloxacin-protected gold nanoparticles. Langmuir. 2004;20(5):1909–1914. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

