A multicenter, open-label, phase 2 study of lenalidomide plus low-dose dexamethasone in Chinese patients with relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma: the MM-021 trial
- PMID: 23782711
- PMCID: PMC3699390
- DOI: 10.1186/1756-8722-6-41
A multicenter, open-label, phase 2 study of lenalidomide plus low-dose dexamethasone in Chinese patients with relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma: the MM-021 trial
Abstract
Background: There is an unmet need for treatment options in Chinese patients with relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma (RRMM). Lenalidomide plus low-dose dexamethasone is effective and generally well tolerated in Caucasian RRMM patients, but no previous study has evaluated this regimen in Chinese RRMM patients.
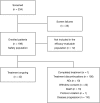
Methods: MM-021 is a phase 2, multicenter, single-arm open-label registration trial conducted to assess the efficacy, safety, and pharmacokinetics of lenalidomide plus low-dose dexamethasone in Chinese patients with RRMM. Patients with ≥1 prior antimyeloma therapy received lenalidomide plus low-dose dexamethasone until disease progression or discontinuation. Follow-up of surviving patients continued for ≥1 year after enrollment. The lenalidomide dose was 25 mg/day, and was adjusted according to baseline renal function. Most patients had advanced disease (85.6% had Durie-Salmon stage III) and were heavily pretreated (56.7% had received ≥4 prior regimens; 69.5% prior thalidomide and 63.1% prior bortezomib); 5.3% had immunoglobulin D (IgD) disease.
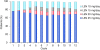
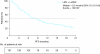
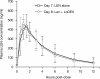
Results: The safety population comprised 199 eligible patients. In the efficacy population (n = 187), the disease control rate (at least stable disease) was 94.7%, and the overall response rate (at least partial response) was 47.6%. High response rates were also achieved in patients who had renal impairment and in those with IgD disease. After a median study follow-up of 15.2 months, the median response duration was 8.8 months (range, 0.4-18.8 months) and median progression-free survival was 8.3 months (95% CI 6.5-9.8). The most common grade 3-4 adverse events (AEs) were anemia (26.1%), neutropenia (25.1%), thrombocytopenia (14.6%), pneumonia (13.1%), leukopenia (9.5%), and decreased neutrophil count (8.5%). AEs led to lenalidomide dose reduction and/or interruption in 40.2% of patients, and treatment discontinuation in about 9% of patients. The pharmacokinetic profile of lenalidomide was similar to that reported in Caucasian and Japanese patients.
Conclusions: Lenalidomide plus low-dose dexamethasone was associated with a high response rate and acceptable safety profile in heavily pretreated Chinese patients with RRMM, including those with renal impairment and IgD subtype. These findings highlight the clinical potential of this regimen in Chinese RRMM patients who have exhausted current treatment options.
Trial registration: China State Food and Drug Administration (SFDA) registration (CTA reference numbers: 209 L10808; 209 L10809; 209 L10810; and 209 L10811) and ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT01593410.
Figures
References
-
- Chen N, Lau H, Kong L. Chinese tumor annual registry of 2004 (edited by the National office of cancer prevention and treatment, National center for cancer registry, Bureau of disease control and prevention of the ministry of health) Chinese Union Medical College; 2004. p. 60.
-
- Liu E, Xiang Y, Jin F, Zhou S, Sun L, Fang R, Yuan Z, Gao L, Gao Y. Analysis of the trend of incidence of malignant tumors in Shanghai region (from years 1972–1999) Tumor. 2004;24:11–15.
-
- Qiu L. The treatment of multiple myeloma: current status and progress. Chin J Pract Intern Med. 2006;26:886–888.
-
- Chinese Multiple Myeloma Working Group. China treatment guideline for multiple myeloma. Chin J Intern Med. 2008;47:869–872.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

