PARP-1 regulates metastatic melanoma through modulation of vimentin-induced malignant transformation
- PMID: 23785295
- PMCID: PMC3681683
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003531
PARP-1 regulates metastatic melanoma through modulation of vimentin-induced malignant transformation
Abstract
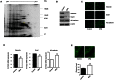
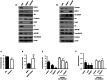
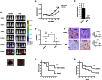
PARP inhibition can induce anti-neoplastic effects when used as monotherapy or in combination with chemo- or radiotherapy in various tumor settings; however, the basis for the anti-metastasic activities resulting from PARP inhibition remains unknown. PARP inhibitors may also act as modulators of tumor angiogenesis. Proteomic analysis of endothelial cells revealed that vimentin, an intermediary filament involved in angiogenesis and a specific hallmark of EndoMT (endothelial to mesenchymal transition) transformation, was down-regulated following loss of PARP-1 function in endothelial cells. VE-cadherin, an endothelial marker of vascular normalization, was up-regulated in HUVEC treated with PARP inhibitors or following PARP-1 silencing; vimentin over-expression was sufficient to drive to an EndoMT phenotype. In melanoma cells, PARP inhibition reduced pro-metastatic markers, including vasculogenic mimicry. We also demonstrated that vimentin expression was sufficient to induce increased mesenchymal/pro-metastasic phenotypic changes in melanoma cells, including ILK/GSK3-β-dependent E-cadherin down-regulation, Snail1 activation and increased cell motility and migration. In a murine model of metastatic melanoma, PARP inhibition counteracted the ability of melanoma cells to metastasize to the lung. These results suggest that inhibition of PARP interferes with key metastasis-promoting processes, leading to suppression of invasion and colonization of distal organs by aggressive metastatic cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures




References
-
- Baum B, Settleman J, Quinlan MP (2008) Transitions between epithelial and mesenchymal states in development and disease. Semin Cell Dev Biol 19: 294–308. - PubMed
-
- Carmeliet P, Jain RK (2000) Angiogenesis in cancer and other diseases. Nature 407: 249–257. - PubMed
-
- Vestweber D, Winderlich M, Cagna G, Nottebaum AF (2009) Cell adhesion dynamics at endothelial junctions: VE-cadherin as a major player. Trends Cell Biol 19: 8–15. - PubMed
-
- Radisky DC (2005) Epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Cell Sci 118: 4325–4326. - PubMed
-
- Hugo H, Ackland ML, Blick T, Lawrence MG, Clements JA, et al. (2007) Epithelial–mesenchymal and mesenchymal–epithelial transitions in carcinoma progression. J Cell Physiol 213: 374–383. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

