BMS1 is mutated in aplasia cutis congenita
- PMID: 23785305
- PMCID: PMC3681727
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003573
BMS1 is mutated in aplasia cutis congenita
Abstract
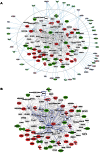
Aplasia cutis congenita (ACC) manifests with localized skin defects at birth of unknown cause, mostly affecting the scalp vertex. Here, genome-wide linkage analysis and exome sequencing was used to identify the causative mutation in autosomal dominant ACC. A heterozygous Arg-to-His missense mutation (p.R930H) in the ribosomal GTPase BMS1 is identified in ACC that is associated with a delay in 18S rRNA maturation, consistent with a role of BMS1 in processing of pre-rRNAs of the small ribosomal subunit. Mutations that affect ribosomal function can result in a cell cycle defect and ACC skin fibroblasts with the BMS1 p.R930H mutation show a reduced cell proliferation rate due to a p21-mediated G1/S phase transition delay. Unbiased comparative global transcript and proteomic analyses of ACC fibroblasts with this mutation confirm a central role of increased p21 levels for the ACC phenotype, which are associated with downregulation of heterogenous nuclear ribonucleoproteins (hnRNPs) and serine/arginine-rich splicing factors (SRSFs). Functional enrichment analysis of the proteomic data confirmed a defect in RNA post-transcriptional modification as the top-ranked cellular process altered in ACC fibroblasts. The data provide a novel link between BMS1, the cell cycle, and skin morphogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The author has declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
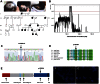
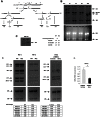
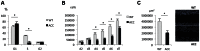
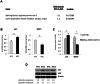
Comment in
-
[BMS1 mutations in aplasia cutis congenita].Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2014 Feb;141(2):161. doi: 10.1016/j.annder.2013.10.034. Epub 2013 Nov 19. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2014. PMID: 24507215 French. No abstract available.
References
-
- Evers ME, Steijlen PM, Hamel BC (1995) Aplasia cutis congenita and associated disorders: an update. Clin Genet 47: 295–301. - PubMed
-
- Zenker M, Mayerle J, Lerch MM, Tagariello A, Zerres K, et al. (2005) Deficiency of UBR1, a ubiquitin ligase of the N-end rule pathway, causes pancreatic dysfunction, malformations and mental retardation (Johanson-Blizzard syndrome). Nat Genet 37: 1345–1350. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

