Sinus histiocytosis (Rosai-Dorfman disease) presenting with solitary cutaneous nodule: a very rare clinical entity
- PMID: 23785592
- PMCID: PMC3663349
- DOI: 10.5826/dpc.0202a04
Sinus histiocytosis (Rosai-Dorfman disease) presenting with solitary cutaneous nodule: a very rare clinical entity
Abstract
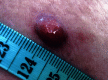
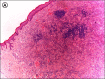
Sinus histiocytosis is a rare inflammatory disease mainly affecting the cervical lymph nodes, presenting with skin lesions in 10% of cases. Our patient had a solitary nodule on the trunk without any other clinical signs. The histology reported a dermal neoplasm composed mainly of macrophages and lymphocytes. Macrophages were aggregated in clusters resembling lymph node sinuses. Lymphophagocytosis or emperipolesis (the presence of an intact cell within the cytoplasm of another cell) was noted and the diagnosis of sinus histiocytosis established.
Keywords: Rosai-Dorfman; histiocytosis; nodule; sinus histiocytosis.
Figures

References
-
- Burgdorf WHC, Plewig G, Wolff HH, et al. Sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy. In: Burgdorf WHC, Plewig G, Wolff HH, et al., editors. Braun-Falco’s Dermatology. 3rd ed. Heidelberg: Springer Medizin Verlag; 2009. pp. 1528–9.
-
- Freedberg IM, Eisen AZ, Wolff K, et al. Sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy. In: Freedberg IM, Eisen AZ, Wolff K, et al., editors. Fitzpatrick’s Dermatology in General Medicine. 6th ed. New York: McGraw Hill Professional; 2003. pp. 1593–4.
-
- Weitzman, Jaffe R. Uncommon histiocytic disorders: the non-Langherhans cell histiocytoses. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2005;45(3):256–64. - PubMed
-
- Flater JL, Maddox JS, Obadiah JM, Hurley MY. Cutaneous Rosai-Dorfman disease: comprehensive review of cases reported in the medical literature since 1990 and presentation of an illustrative case. J Cutan Med Surg. 2006;10(6):281–90. - PubMed
-
- Foucar E, Rosai J, Dorfman R. Sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy (Rosai-Dorfman disease): review of the entity. Semin Diagn Pathol. 1990;7(1):19–73. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
