Systemic mastocytosis associated with chronic myelomonocytic leukemia and xanthogranuloma
- PMID: 23785605
- PMCID: PMC3663351
- DOI: 10.5826/dpc.0203a03
Systemic mastocytosis associated with chronic myelomonocytic leukemia and xanthogranuloma
Abstract
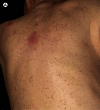
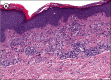
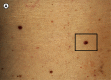
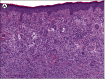
A patient with a history of non-diagnostic bone marrow biopsies presented with a red to brown maculopapular rash on the back. Biopsies confirmed multiple xanthogranulomas as well as a mastocytosis. A consequently performed bone marrow biopsy verified a systemic mastocytosis and a chronic myelomonocytic leukemia (CMML) type I. HERE, WE DESCRIBE FOR THE FIRST TIME IN THE LITERATURE A PATIENT WITH THREE DISEASES OCCURRING SYNCHRONOUSLY: CMML, xanthogranulomas and systemic mastocytosis. Two of them at a time are known to be associated and may be indicative of a common progenitor cell.
Keywords: CMML; Systemic mastocytosis; leukemia; xanthogranuloma.
Figures







References
-
- Travis WD, Li CY, Bergstralh EJ, Yam LT, Swee RG. Systemic mast cell disease. Analysis of 58 cases and literature review. Medicine (Baltimore) 1988;67(6):345–68. - PubMed
-
- Travis WD, Li CY, Yam LT, Bergstralh EJ, Swee RG. Significance of systemic mast cell disease with associated hematologic disorders. Cancer. 1988;62(5):965–72. - PubMed
-
- Lim KH, Tefferi A, Lasho TL, et al. Systemic mastocytosis in 342 consecutive adults: survival studies and prognostic factors. Blood. 2009;113(23):5727–36. - PubMed
-
- Pardanani A, Lim KH, Lasho TL, et al. Prognostically relevant breakdown of 123 patients with systemic mastocytosis associated with other myeloid malignancies. Blood. 2009;114(18):3769–72. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
