Immunotherapy trials for type 1 diabetes: the contribution of George Eisenbarth
- PMID: 23786294
- PMCID: PMC3676656
- DOI: 10.1089/dia.2013.0107
Immunotherapy trials for type 1 diabetes: the contribution of George Eisenbarth
Abstract
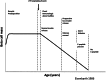
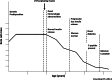
Type 1 diabetes (T1D) results from the autoimmune destruction of pancreatic β-cells, and as such it should respond to immunotherapy. George Eisenbarth gave many significant contributions to this field. He has been involved at some level in most immunotherapy trials during the past three decades. He was among the pioneers who attempted immunotherapy approaches in patients with recent-onset T1D. In the early 1980s he began studying relatives of those with the disease, leading to the concept that T1D was a chronic autoimmune disease, in which islet autoimmune responses would silently destroy β-cells and cause progressive impairment of insulin secretion, years to months before a diagnosis was made. Consequently, he was one of the first to attempt immune intervention in people at high risk of T1D. Throughout his career he developed autoantibody assays and predictive models (which included metabolic testing and later genetics) to identify individuals at risk of T1D. He provided seminal intellectual contributions and critical tools for prevention trials. His focus on insulin as a critical autoantigen led to multiple prevention trials, including the Diabetes Prevention Trial-Type 1 (DPT-1), which studied both parenteral and oral insulin. In the DPT-1 Oral Insulin Trial, a cohort with higher levels of insulin autoantibodies was identified that appeared to have delayed disease progression. Type 1 Diabetes TrialNet is conducting a new trial to verify or refute this observation. Moreover, George identified and tested in the mouse small molecules that block or modulate presentation of a key insulin peptide and in turn prevent the activation of insulin-specific T-lymphocytes. Thus, we believe his greatest contribution is yet to come, as in the near future we should see this most recent work translate into clinical trials.
Figures
References
-
- Bottazzo GF. Florin-Christensen A. Doniach D. Islet-cell antibodies in diabetes mellitus with autoimmune polyendocrine deficiencies. Lancet. 1974;304:1279–1283. - PubMed
-
- Nerup J. Platz P. Andersen OO. Christy M. Lyngsoe J. Poulsen JE. Ryder LP. Nielsen LS. Thomsen M. Svejgaard A. HL-A antigens and diabetes mellitus. Lancet. 1974;304:864–866. - PubMed
-
- Eisenbarth GS. Type I diabetes mellitus. A chronic autoimmune disease. N Engl J Med. 1986;314:1360–1368. - PubMed
-
- Atkinson MA. Eisenbarth GS. Type 1 diabetes: new perspectives on disease pathogenesis and treatment. Lancet. 2001;358:221–229. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

