Role of caveolae in shear stress-mediated endothelium-dependent dilation in coronary arteries
- PMID: 23787000
- PMCID: PMC3778958
- DOI: 10.1093/cvr/cvt157
Role of caveolae in shear stress-mediated endothelium-dependent dilation in coronary arteries
Abstract
Aims: Caveolae are membrane microdomains where important signalling pathways are assembled and molecular effects transduced. In this study, we hypothesized that shear stress-mediated vasodilation (SSD) of mouse small coronary arteries (MCA) is caveolae-dependent.
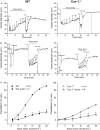
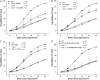
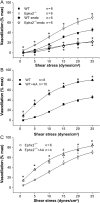
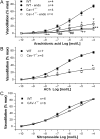
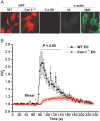
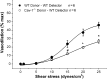
Methods and results: MCA (80-150 μm) isolated from wild-type (WT) and caveolin-1 null (Cav-1(-/-)) mice were subjected to physiological levels of shear stress (1-25 dynes/cm(2)) with and without pre-incubation of inhibitors of nitric oxide synthase (L-NAME), cyclooxygenase (indomethacin, INDO), or cytochrome P450 epoxygenase (SKF 525A). SSD was endothelium-dependent in WT and Cav-1(-/-) coronaries but that in Cav-1(-/-) was significantly diminished compared with WT. Pre-incubation with L-NAME, INDO, or SKF 525A significantly reduced SSD in WT but not in Cav-1(-/-) mice. Vessels from the soluble epoxide hydrolase null (Ephx2(-/-)) mice showed enhanced SSD, which was further augmented by the presence of arachidonic acid. In donor-detector-coupled vessel experiments, Cav-1(-/-) donor vessels produced diminished dilation in WT endothelium-denuded detector vessels compared with WT donor vessels. Shear stress elicited a robust intracellular Ca(2+) increase in vascular endothelial cells isolated from WT but not those from Cav-1(-/-) mice.
Conclusion: Integrity of caveolae is critical for endothelium-dependent SSD in MCA. Cav-1(-/-) endothelium is deficient in shear stress-mediated generation of vasodilators including NO, prostaglandins, and epoxyeicosatrienoic acids. Caveolae plays a critical role in endothelial signal transduction from shear stress to vasodilator production and release.
Keywords: Calcium; Caveolae; Coronary artery; Shear stress; Soluble epoxide hydrolase.
Figures
References
-
- Razani B, Woodman SE, Lisanti MP. Caveolae: from cell biology to animal physiology. Pharmacol Rev. 2002;54:431–467. - PubMed
-
- Gratton JP, Bernatchez P, Sessa WC. Caveolae and caveolins in the cardiovascular system. Circulation Research. 2004;94:1408–1417. - PubMed
-
- Shaw L, Sweeney MA, O'Neill SC, Jones CJ, Austin C, Taggart MJ. Caveolae and sarcoplasmic reticular coupling in smooth muscle cells of pressurised arteries: the relevance for Ca2+ oscillations and tone. Cardiovasc Res. 2006;69:825–835. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

