Structure-based approach to alter the substrate specificity of Bacillus subtilis aminopeptidase
- PMID: 23787698
- PMCID: PMC3904319
- DOI: 10.4161/pri.25147
Structure-based approach to alter the substrate specificity of Bacillus subtilis aminopeptidase
Abstract
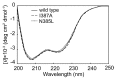
Aminopeptidases can selectively catalyze the cleavage of the N-terminal amino acid residues from peptides and proteins. Bacillus subtilis aminopeptidase (BSAP) is most active toward p-nitroanilides (pNAs) derivatives of Leu, Arg, and Lys. The BSAP with broad substrate specificity is expected to improve its application. Based on an analysis of the predicted structure of BSAP, four residues (Leu 370, Asn 385, Ile 387, and Val 396) located in the substrate binding region were selected for saturation mutagenesis. The hydrolytic activity toward different aminoacyl-pNAs of each mutant BSAP in the culture supernatant was measured. Although the mutations resulted in a decrease of hydrolytic activity toward Leu-pNA, N385L BSAP exhibited higher hydrolytic activities toward Lys-pNA (2.2-fold) and Ile-pNA (9.1-fold) than wild-type BSAP. Three mutant enzymes (I387A, I387C and I387S BSAPs) specially hydrolyzed Phe-pNA, which was undetectable in wild-type BSAP. Among these mutant BSAPs, N385L and I387A BSAPs were selected for further characterized and used for protein hydrolysis application. Both of N385L and I387A BSAPs showed higher hydrolysis efficiency than the wild-type BASP and a combination of the wild-type and N385L and I387A BSAPs exhibited the highest hydrolysis efficiency for protein hydrolysis. This study will greatly facilitate studies aimed on change the substrate specificity and our results obtained here should be useful for BSAP application in food industry.
Keywords: Bacillus subtilis; aminopeptidase; protein hydrolysis; saturation mutagenesis; substrate specificity.
Figures



References
-
- Kilcawley KN, Wilkinson MG, Fox PF. Determination of key enzyme activities in commercial peptidase and lipase preparations from microbial or animal sources. Enzyme Microb Technol. 2002;31:310–20. doi: 10.1016/S0141-0229(02)00136-9. - DOI
-
- Taylor A. Aminopeptidases: towards a mechanism of action. Trends Biochem Sci. 1993;18:167–71. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
