Evolution of deceptive and true courtship songs in moths
- PMID: 23788180
- PMCID: PMC3687589
- DOI: 10.1038/srep02003
Evolution of deceptive and true courtship songs in moths
Abstract
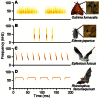
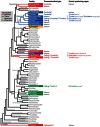
Ultrasonic mating signals in moths are argued to have evolved via exploitation of the receivers' sensory bias towards bat echolocation calls. We have demonstrated that female moths of the Asian corn borer are unable to distinguish between the male courtship song and bat calls. Females react to both the male song and bat calls by "freezing", which males take advantage of in mating (deceptive courtship song). In contrast, females of the Japanese lichen moth are able to distinguish between the male song and bat calls by the structure of the sounds; females emit warning clicks against bats, but accept males (true courtship song). Here, we propose a hypothesis that deceptive and true signals evolved independently from slightly different precursory sounds; deceptive/true courtship songs in moths evolved from the sounds males incidentally emitted in a sexual context, which females could not/could distinguish, respectively, from bat calls.
Figures



References
-
- Endler J. A. & Basolo A. Sensory ecology, receiver biases and sexual selection. Trend Ecol Evol 13, 415–420 (1998). - PubMed
-
- Ryan M. J. Sexual selection, receiver biases, and the evolution of sex differences. Science 281, 1999–2003 (1998). - PubMed
-
- Greenfield M. D. Signallers and Receivers: Mechanisms and Evolution of Arthropod Communication (Oxford Univ. Press, Oxford, 2002).
-
- Garcia C. M. & Ramirez E. Evidence that sensory traps can evolve into honest signals. Nature 434, 501–505 (2005). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

