Age and sex patterns of drug prescribing in a defined American population
- PMID: 23790544
- PMCID: PMC3754826
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mayocp.2013.04.021
Age and sex patterns of drug prescribing in a defined American population
Abstract
Objective: To describe the age and sex patterns of drug prescribing in Olmsted County, Minnesota.
Patients and methods: Population-based drug prescription records for the Olmsted County population in 2009 were obtained using the Rochester Epidemiology Project medical records linkage system (n=142,377). Drug prescriptions were classified using RxNorm codes and were grouped using the National Drug File-Reference Terminology.
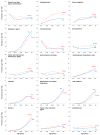
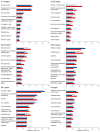
Results: Overall, 68.1% of the population (n=96,953) received a prescription from at least 1 drug group, 51.6% (n=73,501) received prescriptions from 2 or more groups, and 21.2% (n=30,218) received prescriptions from 5 or more groups. The most commonly prescribed drug groups in the entire population were penicillins and β-lactam antimicrobials (17%; n=23,734), antidepressants (13%; n=18,028), opioid analgesics (12%; n=16,954), antilipemic agents (11%; n=16,082), and vaccines/toxoids (11%; n=15,918). However, prescribing patterns differed by age and sex. Vaccines/toxoids, penicillins and β-lactam antimicrobials, and antiasthmatic drugs were most commonly prescribed in persons younger than 19 years. Antidepressants and opioid analgesics were most commonly prescribed in young and middle-aged adults. Cardiovascular drugs were most commonly prescribed in older adults. Women received more prescriptions than men for several drug groups, in particular for antidepressants. For several drug groups, use increased with advancing age.
Conclusion: This study provides valuable baseline information for future studies of drug utilization and drug-related outcomes in this population.
Copyright © 2013 Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Gu Q, Dillon CF, Burt VL. Prescription drug use continues to increase: U.S. prescription drug data for 2007-2008. NCHS Data Brief. 2010:1–8. - PubMed
-
- National Center for Health Statistics. Health, United States, 2011: With Special Feature on Socioeconomic Status and Health. Hyattsville, MD: 2012. [April 12, 2013]. http://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/hus/hus11.pdf. - PubMed
-
- CDC grand rounds: prescription drug overdoses - a U.S. epidemic. [April 12, 2013];MMWR. 2012 61:10–13. http://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/preview/mmwrhtml/mm6101a3.htm. - PubMed
-
- Center for Disease Control (CDC) [April 12, 2013];Unintentional drug poisoning in the United States. http://www.cdc.gov/HomeandRecreationalSafety/pdf/poision-issue-brief.pdf.
-
- Lucado J, Paez K, Elixhauser A. Medication-Related Adverse Outcomes in U.S. Hospitals and Emergency Departments, 2008. HCUP Statistical Brief #109. 2011 http://www.hcup-us.ahrq.gov/reports/statbriefs/sb109.pdf. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

