Terminal axon branching is regulated by the LKB1-NUAK1 kinase pathway via presynaptic mitochondrial capture
- PMID: 23791179
- PMCID: PMC3729210
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.05.021
Terminal axon branching is regulated by the LKB1-NUAK1 kinase pathway via presynaptic mitochondrial capture
Abstract
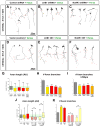
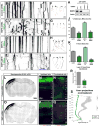
The molecular mechanisms underlying the axon arborization of mammalian neurons are poorly understood but are critical for the establishment of functional neural circuits. We identified a pathway defined by two kinases, LKB1 and NUAK1, required for cortical axon branching in vivo. Conditional deletion of LKB1 after axon specification or knockdown of NUAK1 drastically reduced axon branching in vivo, whereas their overexpression was sufficient to increase axon branching. The LKB1-NUAK1 pathway controls mitochondria immobilization in axons. Using manipulation of Syntaphilin, a protein necessary and sufficient to arrest mitochondrial transport specifically in the axon, we demonstrate that the LKB1-NUAK1 kinase pathway regulates axon branching by promoting mitochondria immobilization. Finally, we show that LKB1 and NUAK1 are necessary and sufficient to immobilize mitochondria specifically at nascent presynaptic sites. Our results unravel a link between presynaptic mitochondrial capture and axon branching.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures





Comment in
-
Carving axon arbors to fit: master directs one kinase at a time.Cell. 2013 Jun 20;153(7):1425-6. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.05.047. Cell. 2013. PMID: 23791171
-
Neural development: Breaking before branching.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2013 Aug;14(8):520. doi: 10.1038/nrn3556. Epub 2013 Jul 10. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23839598 No abstract available.
References
-
- Alessi DR, Sakamoto K, Bayascas JR. LKB1-dependent signaling pathways. Annu Rev Biochem. 2006;75:137–163. - PubMed
-
- Baas AF, Kuipers J, van der Wel NN, Batlle E, Koerten HK, Peters PJ, Clevers HC. Complete polarization of single intestinal epithelial cells upon activation of LKB1 by STRAD. Cell. 2004;116:457–466. - PubMed
-
- Bardeesy N, Sinha M, Hezel AF, Signoretti S, Hathaway NA, Sharpless NE, Loda M, Carrasco DR, DePinho RA. Loss of the Lkb1 tumour suppressor provokes intestinal polyposis but resistance to transformation. Nature. 2002;419:162–167. - PubMed
-
- Barnes AP, Lilley BN, Pan YA, Plummer LJ, Powell AW, Raines AN, Sanes JR, Polleux F. LKB1 and SAD kinases define a pathway required for the polarization of cortical neurons. Cell. 2007;129:549–563. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

