Recombinant probes for visualizing endogenous synaptic proteins in living neurons
- PMID: 23791193
- PMCID: PMC3779638
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2013.04.017
Recombinant probes for visualizing endogenous synaptic proteins in living neurons
Abstract
The ability to visualize endogenous proteins in living neurons provides a powerful means to interrogate neuronal structure and function. Here we generate recombinant antibody-like proteins, termed Fibronectin intrabodies generated with mRNA display (FingRs), that bind endogenous neuronal proteins PSD-95 and Gephyrin with high affinity and that, when fused to GFP, allow excitatory and inhibitory synapses to be visualized in living neurons. Design of the FingR incorporates a transcriptional regulation system that ties FingR expression to the level of the target and reduces background fluorescence. In dissociated neurons and brain slices, FingRs generated against PSD-95 and Gephyrin did not affect the expression patterns of their endogenous target proteins or the number or strength of synapses. Together, our data indicate that PSD-95 and Gephyrin FingRs can report the localization and amount of endogenous synaptic proteins in living neurons and thus may be used to study changes in synaptic strength in vivo.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
One of us (GCRE-D) has filed a preliminary patent declaration on the synthesis of dinitroindolinyl-caged neurotransmitters.
Figures
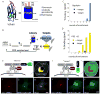
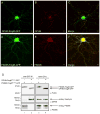
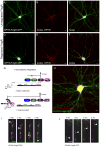
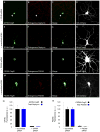
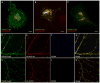
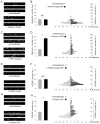
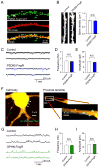
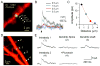
Comment in
-
Protein GPS.Nat Methods. 2013 Aug;10(8):696-7. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.2588. Nat Methods. 2013. PMID: 24058978 No abstract available.
References
-
- Arnold DB, Clapham DE. Molecular determinants for subcellular localization of PSD-95 with an interacting K+ channel. Neuron. 1999;23:149–157. - PubMed
-
- Betzig E, Patterson GH, Sougrat R, Lindwasser OW, Olenych S, Bonifacino JS, Davidson MW, Lippincott-Schwartz J, Hess HF. Imaging intracellular fluorescent proteins at nanometer resolution. Science. 2006;313:1642–1645. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- OD 006117/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R37 NS046579/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS-046579/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- GM 060416/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM060416/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA170820/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI085583/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- MH-086381/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS046579/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS069720/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM053395/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- GM-083898/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- GM53395/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH086381/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM083898/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- NS69720/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS081678/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

