Dendritic cell expression of the signaling molecule TRAF6 is critical for gut microbiota-dependent immune tolerance
- PMID: 23791643
- PMCID: PMC3715143
- DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2013.05.012
Dendritic cell expression of the signaling molecule TRAF6 is critical for gut microbiota-dependent immune tolerance
Abstract
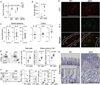
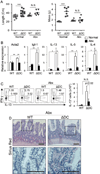
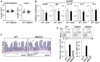
The intracellular signaling molecule TRAF6 is critical for Toll-like receptor (TLR)-mediated activation of dendritic cells (DCs). We now report that DC-specific deletion of TRAF6 (TRAF6ΔDC) resulted, unexpectedly, in loss of mucosal tolerance, characterized by spontaneous development of T helper 2 (Th2) cells in the lamina propria and eosinophilic enteritis and fibrosis in the small intestine. Loss of tolerance required the presence of gut commensal microbiota but was independent of DC-expressed MyD88. Further, TRAF6ΔDC mice exhibited decreased regulatory T (Treg) cell numbers in the small intestine and diminished induction of iTreg cells in response to model antigen. Evidence suggested that this defect was associated with diminished DC expression of interleukin-2 (IL-2). Finally, we demonstrate that aberrant Th2 cell-associated responses in TRAF6ΔDC mice could be mitigated via restoration of Treg cell activity. Collectively, our findings reveal a role for TRAF6 in directing DC maintenance of intestinal immune tolerance through balanced induction of Treg versus Th2 cell immunity.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


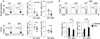
References
-
- Agace WW, Persson EK. How vitamin A metabolizing dendritic cells are generated in the gut mucosa. Trends Immunol. 2012;33:42–48. - PubMed
-
- Atarashi K, Nishimura J, Shima T, Umesaki Y, Yamamoto M, Onoue M, Yagita H, Ishii N, Evans R, Honda K, Takeda K. ATP drives lamina propria T(H)17 cell differentiation. Nature. 2008;455:808–812. - PubMed
-
- Brand S. Crohn’s disease: Th1, Th17 or both? The change of a paradigm: new immunological and genetic insights implicate Th17 cells in the pathogenesis of Crohn’s disease. Gut. 2009;58:1152–1167. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
- U19 AI083022/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI095740/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI095740/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI064909/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI039368/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI037691/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI043620/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI064909/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AI095740/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI039368/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI083022/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI079724/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI079724/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI43620/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI037691/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA016520/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

