Fibronectin and integrin alpha 5 play requisite roles in cardiac morphogenesis
- PMID: 23791818
- PMCID: PMC3833817
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2013.06.010
Fibronectin and integrin alpha 5 play requisite roles in cardiac morphogenesis
Abstract
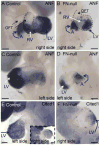
Fibronectin and its major receptor, integrin α5β1 are required for embryogenesis. These mutants have similar phenotypes, although, defects in integrin α5-deficient mice are milder. In this paper, we examined heart development in those mutants, in which the heart is formed, and discovered that both fibronectin and integrin α5 were required for cardiac morphogenesis, and in particular, for the formation of the cardiac outflow tract. We found that Isl1+ precursors are specified and migrate into the heart in fibronectin- or integrin α5-mutant embryos, however, the hearts in these mutants are of aberrant shape, and the cardiac outflow tracts are short and malformed. We show that these defects are likely due to the requirement for cell adhesion to fibronectin for proliferation of myocardial progenitors and for Fgf8 signaling in the pharyngeal region.
Keywords: Cardiac; Fibronectin; Heart; Integrin a5; Morphogenesis; Outflow tract.
Copyright © 2013 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Fibronectin signals through integrin α5β1 to regulate cardiovascular development in a cell type-specific manner.Dev Biol. 2015 Nov 15;407(2):195-210. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2015.09.016. Epub 2015 Oct 3. Dev Biol. 2015. PMID: 26434918 Free PMC article.
-
Cell-Extracellular Matrix Interactions Play Multiple Essential Roles in Aortic Arch Development.Circ Res. 2021 Feb 5;128(3):e27-e44. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.120.318200. Epub 2020 Nov 30. Circ Res. 2021. PMID: 33249995 Free PMC article.
-
Fibronectin and integrin alpha 5 play essential roles in the development of the cardiac neural crest.Mech Dev. 2010 Sep-Dec;127(9-12):472-84. doi: 10.1016/j.mod.2010.08.005. Epub 2010 Aug 31. Mech Dev. 2010. PMID: 20807571 Free PMC article.
-
Snail modulates the assembly of fibronectin via α5 integrin for myocardial migration in zebrafish embryos.Sci Rep. 2014 Mar 26;4:4470. doi: 10.1038/srep04470. Sci Rep. 2014. PMID: 24667151 Free PMC article.
-
Myocyte proliferation in the developing heart.Dev Dyn. 2011 Jun;240(6):1322-34. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.22650. Epub 2011 May 2. Dev Dyn. 2011. PMID: 21538685 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Hypoplastic left heart syndrome (HLHS): molecular pathogenesis and emerging drug targets for cardiac repair and regeneration.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2021 Aug;25(8):621-632. doi: 10.1080/14728222.2021.1978069. Epub 2021 Sep 15. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2021. PMID: 34488532 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intrinsic Endocardial Defects Contribute to Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome.Cell Stem Cell. 2020 Oct 1;27(4):574-589.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2020.07.015. Epub 2020 Aug 17. Cell Stem Cell. 2020. PMID: 32810435 Free PMC article.
-
Single-Cell RNA-Seq Identifies Dynamic Cardiac Transition Program from ADCs Induced by Leukemia Inhibitory Factor.Stem Cells. 2022 Oct 21;40(10):932-948. doi: 10.1093/stmcls/sxac048. Stem Cells. 2022. PMID: 35896368 Free PMC article.
-
Fibronectin signals through integrin α5β1 to regulate cardiovascular development in a cell type-specific manner.Dev Biol. 2015 Nov 15;407(2):195-210. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2015.09.016. Epub 2015 Oct 3. Dev Biol. 2015. PMID: 26434918 Free PMC article.
-
ITGAV and ITGA5 diversely regulate proliferation and adipogenic differentiation of human adipose derived stem cells.Sci Rep. 2016 Jul 1;6:28889. doi: 10.1038/srep28889. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27363302 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Astrof S. Interactions between neural crest-derived cells and extracellular microenvironment during cardiovascular development. In: Desimone DW, Mecham RP, editors. Extracellular Matrix in Development. Springer Verlag; Berlin: 2013. pp. 105–131.
-
- Astrof S, Kirby A, Lindblad-Toh K, Daly M, Hynes RO. Heart development in fibronectin-null mice is governed by a genetic modifier on chromosome four. Mech Dev. 2007;124:551–558. - PubMed
-
- Aszodi A, Legate KR, Nakchbandi I, Fassler R. What mouse mutants teach us about extracellular matrix function. Annual review of cell and developmental biology. 2006;22:591–621. - PubMed
-
- Engler AJ, Sen S, Sweeney HL, Discher DE. Matrix elasticity directs stem cell lineage specification. Cell. 2006;126:677–689. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

