Correlated sodium and potassium imbalances within the ischemic core in experimental stroke: a 23Na MRI and histochemical imaging study
- PMID: 23792152
- PMCID: PMC3885320
- DOI: 10.1016/j.brainres.2013.06.012
Correlated sodium and potassium imbalances within the ischemic core in experimental stroke: a 23Na MRI and histochemical imaging study
Abstract
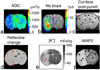
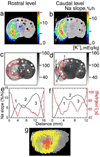
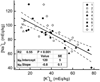
This study addresses the spatial relation between local Na(+) and K(+) imbalances in the ischemic core in a rat model of focal ischemic stroke. Quantitative [Na(+)] and [K(+)] brain maps were obtained by (23)Na MRI and histochemical K(+) staining, respectively, and calibrated by emission flame photometry of the micropunch brain samples. Stroke location was verified by diffusion MRI, by changes in tissue surface reflectivity and by immunohistochemistry with microtubule-associated protein 2 antibody. Na(+) and K(+) distribution within the ischemic core was inhomogeneous, with the maximum [Na(+)] increase and [K(+)] decrease typically observed in peripheral regions of the ischemic core. The pattern of the [K(+)] decrease matched the maximum rate of [Na(+)] increase ('slope'). Some residual mismatch between the sites of maximum Na(+) and K(+) imbalances was attributed to the different channels and pathways involved in transport of the two ions. A linear regression of the [Na(+)]br vs. [K(+)]br in the samples of ischemic brain indicates that for each K(+) equivalent leaving ischemic tissue, 0.8±0.1 Eq, on average, of Na(+) enter the tissue. Better understanding of the mechanistic link between the Na(+) influx and K(+) egress would validate the (23)Na MRI slope as a candidate biomarker and a complementary tool for assessing ischemic damage and treatment planning.
Keywords: (23)Na MRI; 3D; ADC; BBB; Focal ischemia; MAP2; MCA, MCAO, MCAT; Permanent MCAO; RF; ROI; Rat brain; Tissue potassium; Tissue sodium; [Na(+)](br) and [K(+)](br); apparent diffusion coefficient; blood–brain barrier; brain tissue sodium and potassium concentration, respectively; microtubule-associated protein 2; middle cerebral artery, MCA occlusion, and MCA transection with bilateral common carotid artery occlusion, respectively; radiofrequency; region of interest; three-dimensional.
Copyright © 2013. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Figures


References
-
- Belayev L, Alonso OF, Busto R, Zhao W, Ginsberg MD. Middle cerebral artery occlusion in the rat by intraluminal suture. Neurological and pathological evaluation of an improved model. Stroke. 1996;27:1616–1622. - PubMed
-
- Betz AL, Keep RF, Beer ME, Ren X. Blood-brain barrier permeability and brain concentration of sodium, potassium, and chloride during focal ischemia. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 1994;14:29–37. - PubMed
-
- Boada FE, Gillen JS, Noll DC, Shen GX, Chang SY, Thulborn KR. Data acquisition and postprocessing strategies for fast quantitative sodium imaging. Int. J. Imaging Syst. Technol. 1997a;8:544–550.
-
- Boada FE, Gillen JS, Shen GX, Chang SY, Thulborn KR. Fast three dimensional sodium imaging. Magn. Reson. Med. 1997b;37:706–715. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

