Enhancer-derived RNAs: 'spicing up' transcription programs
- PMID: 23792424
- PMCID: PMC3730232
- DOI: 10.1038/emboj.2013.151
Enhancer-derived RNAs: 'spicing up' transcription programs
Abstract
Nature 498, 511–515 doi:; DOI: 10.1038/nature12209; published online May 02 2013
Nature 498, 516–520 doi:; DOI: 10.1038/nature12210; published online May 02 2013
Recent reports established transcription of enhancer-derived RNAs (eRNAs), while the evidence for their functional significance remained mostly speculative. Two recent reports published in Nature (Lam et al, 2013; Li et al, 2013) offer the first functional evidence for eRNA transcripts. These analyses further reveal an unexpected level of specificity in the regulation of adjacent mRNAs by eRNAs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
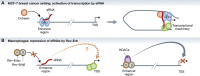
Comment on
-
Functional roles of enhancer RNAs for oestrogen-dependent transcriptional activation.Nature. 2013 Jun 27;498(7455):516-20. doi: 10.1038/nature12210. Epub 2013 Jun 2. Nature. 2013. PMID: 23728302 Free PMC article.
-
Rev-Erbs repress macrophage gene expression by inhibiting enhancer-directed transcription.Nature. 2013 Jun 27;498(7455):511-5. doi: 10.1038/nature12209. Epub 2013 Jun 2. Nature. 2013. PMID: 23728303 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Heintzman ND, Hon GC, Hawkins RD, Kheradpour P, Stark A, Harp LF, Ye Z, Lee LK, Stuart RK, Ching CW, Ching KA, Antosiewicz-Bourget JE, Liu H, Zhang X, Green RD, Lobanenkov VV, Stewart R, Thomson JA, Crawford GE, Kellis M et al. (2009) Histone modifications at human enhancers reflect global cell-type-specific gene expression. Nature 459: 108–112 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

