Obesity, diabetes, and survival outcomes in a large cohort of early-stage breast cancer patients
- PMID: 23793035
- PMCID: PMC3784334
- DOI: 10.1093/annonc/mdt224
Obesity, diabetes, and survival outcomes in a large cohort of early-stage breast cancer patients
Abstract
Background: To determine the relationship between obesity, diabetes, and survival in a large cohort of breast cancer patients receiving modern chemotherapy and endocrine therapy.
Patients and methods: We identified 6342 patients with stage I-III breast cancer treated between 1996 and 2005. Patients were evaluated according to body mass index (BMI) category and diabetes status.
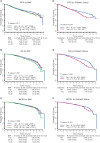
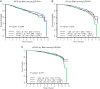
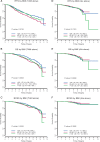
Results: In a multivariate model adjusted for body mass index, diabetes, medical comorbidities, patient- and tumor-related variables, and adjuvant therapies, relative to the normal weight, hazard ratios (HRs) for recurrence-free survival (RFS), overall survival (OS), and breast cancer-specific survival (BCSS) for the overweight were 1.18 [95% confidence interval (CI) 1.02-1.36], 1.20 (95% CI 1.00-1.42), and 1.21 (95% CI 0.98-1.48), respectively. HRs for RFS, OS, and BCSS for the obese were 1.13 (95% CI 0.98-1.31), 1.24 (95% CI 1.04-1.48), and 1.23 (95% CI 1.00-1.52), respectively. Subset analyses showed these differences were significant for the ER-positive, but not ER-negative or HER2-positive, groups. Relative to nondiabetics, HRs for diabetics for RFS, OS, and BCSS were 1.21 (95% CI 0.98-1.49), 1.39 (95% CI 1.10-1.77), and 1.04 (95% CI 0.75-1.45), respectively.
Conclusions: In patients receiving modern adjuvant therapies, obesity has a negative impact on RFS, OS, and BCSS; and diabetes has a negative impact on RFS and OS. Control of both may be important to improving survival in obese and diabetic breast cancer patients.
Keywords: body mass index; breast cancer; diabetes; obesity; prognosis; survival outcomes.
Figures
References
-
- Flegal KM, Carroll MD, Ogden CL, et al. Prevalence and trends in obesity among US adults, 1999–2008. JAMA. 2010;303:235–241. - PubMed
-
- van den Brandt PA, Spiegelman D, Yaun SS, et al. Pooled analysis of prospective cohort studies on height, weight, and breast cancer risk. Am J Epidemiol. 2000;152:514–527. - PubMed
-
- Trentham-Dietz A, Newcomb PA, Storer BE, et al. Body size and risk of breast cancer. Am J Epidemiol. 1997;145:1011–1019. - PubMed
-
- Key TJ, Appleby PN, Reeves GK, et al. Body mass index, serum sex hormones, and breast cancer risk in postmenopausal women. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2003;95:1218–1226. - PubMed
-
- Ewertz M, Jensen MB, Gunnarsdottir KA, et al. Effect of obesity on prognosis after early-stage breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29:25–31. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

