CAY10593 inhibits the human P2X7 receptor independently of phospholipase D1 stimulation
- PMID: 23793974
- PMCID: PMC3889394
- DOI: 10.1007/s11302-013-9371-6
CAY10593 inhibits the human P2X7 receptor independently of phospholipase D1 stimulation
Abstract
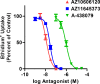
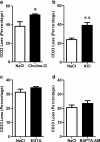
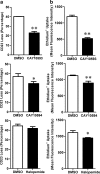
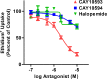
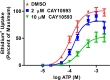
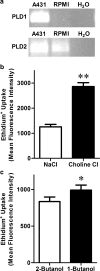
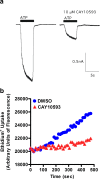
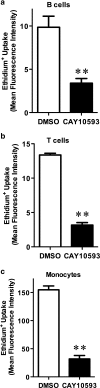
The P2X7 receptor is a trimeric ATP-gated cation channel important in health and disease. We have observed that the specific phospholipase D (PLD)1 antagonist, CAY10593 impairs P2X7-induced shedding of the 'low affinity' IgE receptor, CD23. The current study investigated the mode of action of this compound on P2X7 activation. Measurements of ATP-induced ethidium(+) uptake revealed that CAY10593 impaired P2X7-induced pore formation in human RPMI 8226 B cells, P2X7-transfected HEK-293 cells and peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Concentration response curves demonstrated that CAY10593 impaired P2X7-induced pore formation in RPMI 8226 cells more potently than the PLD2 antagonist CAY10594 and the non-specific PLD antagonist halopemide. Electrophysiology measurements demonstrated that CAY10593 also inhibited P2X7-induced inward currents. Notably, RT-PCR demonstrated that PLD1 was absent in RPMI 8226 cells, while choline-Cl medium or 1-butanol, which block PLD stimulation and signalling respectively did not impair P2X7 activation in these cells. This data indicates that CAY10593 impairs human P2X7 independently of PLD1 stimulation and highlights the importance of ensuring that compounds used in signalling studies downstream of P2X7 activation do not affect the receptor itself.
Figures
References
-
- Wiley JS, Gargett CE, Zhang W, Snook MB, Jamieson GP. Partial agonists and antagonists reveal a second permeability state of human lymphocyte P2Z/P2X7 channel. Am J Physiol. 1998;275:C1224–C1231. - PubMed
-
- Marques-da-Silva C, Chaves MM, Castro NG, Coutinho-Silva R, Guimaraes MZ. Colchicine inhibits cationic dye uptake induced by ATP in P2X2 and P2X7 receptor-expressing cells: implications for its therapeutic action. Br J Pharmacol. 2011;163:912–926. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01254.x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

