Effect of tolcapone on brain activity during a variable attentional control task: a double-blind, placebo-controlled, counter-balanced trial in healthy volunteers
- PMID: 23794107
- PMCID: PMC4135358
- DOI: 10.1007/s40263-013-0082-x
Effect of tolcapone on brain activity during a variable attentional control task: a double-blind, placebo-controlled, counter-balanced trial in healthy volunteers
Abstract
Background: Attention is the capacity to flexibly orient behaviors and thoughts towards a goal by selecting and integrating relevant contextual information. The dorsal cingulate (dCC) and prefrontal (PFC) cortices play critical roles in attention. Evidence indicates that catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT) modulates dopaminergic tone in the PFC and dCC.
Objective: In this study, we explored the effect of tolcapone, a CNS penetrant COMT inhibitor that increases cortical dopamine levels, on brain activity during a Variable Attentional Control (VAC) task.
Study design: We performed a double-blinded, placebo-controlled, counter-balanced trial with tolcapone (Tasmar, tablets, 100 mg three times a day for 1 day and then 200 mg three times a day for 6 days; ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT00044083).
Setting: The study was conducted in the Clinical Center of the National Institute of Mental Health from 2005 to 2009.
Patients: Twenty healthy volunteers (11 males; mean age = 32.7 years) with good imaging and performance data on both arms of the study were investigated.
Intervention: Participants underwent 3T blood-oxygen-level-dependent (BOLD) functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) while performing the event-related VAC task, which varies attention over three levels of load: LOW, INT (intermediate), and HIGH.
Main outcome measure: Changes in behavioral data and individual contrast images were analyzed using ANOVA with drug and task load as co-factors.
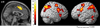
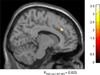
Results: There was a significant main effect of increasing task load, with resulting decreased accuracy and increased reaction time. While there was no significant effect of tolcapone on these behavioral measures, the neuroimaging data showed a significant effect on load-related changes in dCC, with significantly lower dCC activation on tolcapone compared with placebo. Further, neural activity in dCC correlated positively with COMT enzyme activity (i.e., lower COMT activity and presumably more dopamine was associated with lower activation in dCC, i.e., more efficient information processing).
Conclusion: Our results show that pharmacological reduction of COMT activity modulates the engagement of attentional mechanisms, selectively enhancing the efficiency of dCC processing in healthy volunteers, reflected as decreased activity for the same level of performance.
Conflict of interest statement
Sophia C. Magalona, Roberta Rasetti, Jingshan Chen, Qiang Chen, Ian Gold, Heather Decot, Joseph H. Callicott, Karen F. Berman, José A. Apud, Daniel R. Weinberger, and Venkata S. Mattay declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

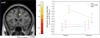
Similar articles
-
Effects of tolcapone on working memory and brain activity in abstinent smokers: a proof-of-concept study.Drug Alcohol Depend. 2013 Dec 15;133(3):852-6. doi: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2013.09.003. Epub 2013 Sep 14. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2013. PMID: 24095246 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Improvement of prepulse inhibition and executive function by the COMT inhibitor tolcapone depends on COMT Val158Met polymorphism.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2008 Dec;33(13):3058-68. doi: 10.1038/npp.2008.82. Epub 2008 Jun 4. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2008. PMID: 18536698 Clinical Trial.
-
Tolcapone improves cognition and cortical information processing in normal human subjects.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2007 May;32(5):1011-20. doi: 10.1038/sj.npp.1301227. Epub 2006 Oct 25. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2007. PMID: 17063156 Clinical Trial.
-
Pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and tolerability of tolcapone: a review of early studies in volunteers.Neurology. 1998 May;50(5 Suppl 5):S31-8. doi: 10.1212/wnl.50.5_suppl_5.s31. Neurology. 1998. PMID: 9591520 Review.
-
General properties and clinical possibilities of new selective inhibitors of catechol O-methyltransferase.Gen Pharmacol. 1994 Sep;25(5):813-24. doi: 10.1016/0306-3623(94)90082-5. Gen Pharmacol. 1994. PMID: 7835624 Review.
Cited by
-
Cortical dopamine reduces the impact of motivational biases governing automated behaviour.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2022 Jul;47(8):1503-1512. doi: 10.1038/s41386-022-01291-8. Epub 2022 Mar 8. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2022. PMID: 35260787 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of Pharmacological Interventions on the Fronto-Cingulo-Parietal Cognitive Control Network in Psychiatric Disorders: A Transdiagnostic Systematic Review of fMRI Studies.Front Psychiatry. 2016 May 18;7:82. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2016.00082. eCollection 2016. Front Psychiatry. 2016. PMID: 27242552 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Systems pharmacogenomics - gene, disease, drug and placebo interactions: a case study in COMT.Pharmacogenomics. 2019 May;20(7):529-551. doi: 10.2217/pgs-2019-0001. Pharmacogenomics. 2019. PMID: 31124409 Free PMC article.
-
Can magnetic resonance imaging enhance the assessment of potential new treatments for cognitive impairment in mood disorders? A systematic review and position paper by the International Society for Bipolar Disorders Targeting Cognition Task Force.Bipolar Disord. 2022 Sep;24(6):615-636. doi: 10.1111/bdi.13247. Epub 2022 Sep 22. Bipolar Disord. 2022. PMID: 35950925 Free PMC article.
-
Tolcapone-Enhanced Neurocognition in Healthy Adults: Neural Basis and Predictors.Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2017 Dec 1;20(12):979-987. doi: 10.1093/ijnp/pyx074. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2017. PMID: 29020372 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- MacDonald AWI, Cohen JD, Stenger VA, Carter CS. Dissociating the role of the dorsolateral prefrontal and anterior cingulate cortex in cognitive control. Science. 2000;288(5472):1835–1838. - PubMed
-
- Durston S, Davidson MC, Thomas KM, Worden MS, Tottenham N, Martinez A, et al. Parametric manipulation of conflict and response competition using rapid mixed-trial event-related fMRI. NeuroImage. 2003;20(4):2135–2141. - PubMed
-
- Blasi G, Goldberg TE, Elveva˚g B, Rasetti R, Bertolino A, Cohen J, et al. Differentiating allocation of resources and conflict detection within attentional control processing. Eur J Neurosci. 2007;25(2):594–602. - PubMed
-
- Weissman DH, Giesbrecht B, Song AW, Mangun GR, Woldorff MG. Conflict monitoring in the human anterior cingulate cortex during selective attention to global and local object features. Neuroimage. 2003;19(4):1361–1368. - PubMed
-
- Kerns JG, Cohen JD, MacDonald AW3, Cho RY, Stenger VA, Carter CS. Anterior cingulate conflict monitoring and adjustments in control. Science. 2004;303(5660):1023–1026. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

