Temporal transcriptional response to ethylene gas drives growth hormone cross-regulation in Arabidopsis
- PMID: 23795294
- PMCID: PMC3679525
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.00675
Temporal transcriptional response to ethylene gas drives growth hormone cross-regulation in Arabidopsis
Abstract
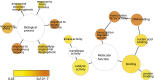
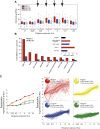
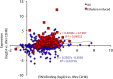
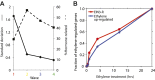
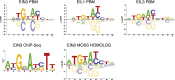
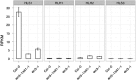
The gaseous plant hormone ethylene regulates a multitude of growth and developmental processes. How the numerous growth control pathways are coordinated by the ethylene transcriptional response remains elusive. We characterized the dynamic ethylene transcriptional response by identifying targets of the master regulator of the ethylene signaling pathway, ETHYLENE INSENSITIVE3 (EIN3), using chromatin immunoprecipitation sequencing and transcript sequencing during a timecourse of ethylene treatment. Ethylene-induced transcription occurs in temporal waves regulated by EIN3, suggesting distinct layers of transcriptional control. EIN3 binding was found to modulate a multitude of downstream transcriptional cascades, including a major feedback regulatory circuitry of the ethylene signaling pathway, as well as integrating numerous connections between most of the hormone mediated growth response pathways. These findings provide direct evidence linking each of the major plant growth and development networks in novel ways. DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.00675.001.
Keywords: Arabidopsis; Physcomitrella patens; ethylene; hormone; network; temporal modulation; transcriptional regulation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Figures





Comment in
-
When the time is ripe.Elife. 2013 Jun 25;2:e00958. doi: 10.7554/eLife.00958. Elife. 2013. PMID: 23840932 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

