Cardiovascular effects of intensive lifestyle intervention in type 2 diabetes
- PMID: 23796131
- PMCID: PMC3791615
- DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa1212914
Cardiovascular effects of intensive lifestyle intervention in type 2 diabetes
Erratum in
- N Engl J Med. 2014 May 8;370(19):1866
Abstract
Background: Weight loss is recommended for overweight or obese patients with type 2 diabetes on the basis of short-term studies, but long-term effects on cardiovascular disease remain unknown. We examined whether an intensive lifestyle intervention for weight loss would decrease cardiovascular morbidity and mortality among such patients.
Methods: In 16 study centers in the United States, we randomly assigned 5145 overweight or obese patients with type 2 diabetes to participate in an intensive lifestyle intervention that promoted weight loss through decreased caloric intake and increased physical activity (intervention group) or to receive diabetes support and education (control group). The primary outcome was a composite of death from cardiovascular causes, nonfatal myocardial infarction, nonfatal stroke, or hospitalization for angina during a maximum follow-up of 13.5 years.
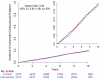
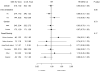
Results: The trial was stopped early on the basis of a futility analysis when the median follow-up was 9.6 years. Weight loss was greater in the intervention group than in the control group throughout the study (8.6% vs. 0.7% at 1 year; 6.0% vs. 3.5% at study end). The intensive lifestyle intervention also produced greater reductions in glycated hemoglobin and greater initial improvements in fitness and all cardiovascular risk factors, except for low-density-lipoprotein cholesterol levels. The primary outcome occurred in 403 patients in the intervention group and in 418 in the control group (1.83 and 1.92 events per 100 person-years, respectively; hazard ratio in the intervention group, 0.95; 95% confidence interval, 0.83 to 1.09; P=0.51).
Conclusions: An intensive lifestyle intervention focusing on weight loss did not reduce the rate of cardiovascular events in overweight or obese adults with type 2 diabetes. (Funded by the National Institutes of Health and others; Look AHEAD ClinicalTrials.gov number, NCT00017953.).
Figures
Comment in
-
Do lifestyle changes reduce serious outcomes in diabetes?N Engl J Med. 2013 Jul 11;369(2):189-90. doi: 10.1056/NEJMe1306987. Epub 2013 Jun 24. N Engl J Med. 2013. PMID: 23796132 No abstract available.
-
Diabetes: Look AHEAD published: weight loss not linked to fewer cardiovascular events in patients with type 2 diabetes.Nat Rev Cardiol. 2013 Aug;10(8):429. doi: 10.1038/nrcardio.2013.101. Epub 2013 Jul 9. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2013. PMID: 23836280 No abstract available.
-
Modest weight loss does not decrease cardiovascular morbidity and mortality in adults with type 2 diabetes.Evid Based Med. 2014 Apr;19(2):64. doi: 10.1136/eb-2013-101518. Epub 2013 Oct 10. Evid Based Med. 2014. PMID: 24113231 No abstract available.
-
ACP Journal Club. A lifestyle intervention did not reduce cardiovascular outcomes in overweight or obese patients with type 2 diabetes.Ann Intern Med. 2013 Oct 15;159(8):JC4. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-159-8-201310150-02004. Ann Intern Med. 2013. PMID: 24126665 No abstract available.
-
Intensive lifestyle intervention in type 2 diabetes.N Engl J Med. 2013 Dec 12;369(24):2358-9. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1312802. N Engl J Med. 2013. PMID: 24328474 No abstract available.
-
Intensive lifestyle intervention in type 2 diabetes.N Engl J Med. 2013 Dec 12;369(24):2356. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1312802. N Engl J Med. 2013. PMID: 24328475 No abstract available.
-
Intensive lifestyle intervention in type 2 diabetes.N Engl J Med. 2013 Dec 12;369(24):2356. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1312802. N Engl J Med. 2013. PMID: 24328476 No abstract available.
-
Intensive lifestyle intervention in type 2 diabetes.N Engl J Med. 2013 Dec 12;369(24):2356-7. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1312802. N Engl J Med. 2013. PMID: 24328477 No abstract available.
-
Intensive lifestyle intervention in type 2 diabetes.N Engl J Med. 2013 Dec 12;369(24):2357. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1312802. N Engl J Med. 2013. PMID: 24328478 No abstract available.
-
Intensive lifestyle intervention in type 2 diabetes.N Engl J Med. 2013 Dec 12;369(24):2357-8. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1312802. N Engl J Med. 2013. PMID: 24328479 No abstract available.
-
Intensive lifestyle intervention has little effect on cardiovascular complications in people with type 2 diabetes.J R Coll Physicians Edinb. 2013;43(4):315. doi: 10.4997/JRCPE.2013.409. J R Coll Physicians Edinb. 2013. PMID: 24350314 No abstract available.
-
[Cardiovascular effects of an intensive intervention on lifestyle in type 2 diabetes].Rev Clin Esp (Barc). 2014 Mar;214(2):102. doi: 10.1016/j.rce.2013.09.003. Rev Clin Esp (Barc). 2014. PMID: 24772473 Spanish. No abstract available.
-
[Cardiovascular effects of a lifestyle intervention in type 2 diabetes. The Look AHEAD (Action for Health in Diabetes) study].Internist (Berl). 2014 Jun;55(6):735-8. doi: 10.1007/s00108-014-3513-y. Internist (Berl). 2014. PMID: 24817540 German. No abstract available.
References
-
- American Diabetes Association . Clinical Practice Recommendations. American Diabetes Association; Alexandria, VA: 2013.
-
- NHLBI Clinical guidelines on the identification, evaluation, and treatment of overweight and obesity in adults-The evidence report. Obes Res. 1998;6(S2):51S–210S. - PubMed
-
- Williamson DF. Weight loss and mortality in persons with type-2 diabetes mellitus: A review of the epidemiological evidence. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 1998;106(Suppl 2):14–21. - PubMed
-
- Harrington M, Gibson S, Cottrell RC. A review and meta-analysis of the effect of weight loss on all-cause mortality risk. Nurt Res Rev. 2009;22(1):93–108. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
- DK57078/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000005/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- DK57151/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK057136/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01RR000056/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- DK56990/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR 024153/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- DK57171/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK57131/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK57149/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK056992/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK079637/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01RR01066/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- DK57182/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK57002/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01RR01346/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- DK57178/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK48520/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK57008/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K23 HL109235/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK057131/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- DK57136/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK57154/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK57219/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK57177/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01RR0021140/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- DK 046204/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK057149/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK57135/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R24 DK084949/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01RR02719/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- DK56992/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK017047/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01RR00051/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical