Weight, inflammation, cancer-related symptoms and health related quality of life among breast cancer survivors
- PMID: 23797178
- PMCID: PMC3772666
- DOI: 10.1007/s10549-013-2594-y
Weight, inflammation, cancer-related symptoms and health related quality of life among breast cancer survivors
Abstract
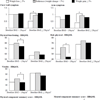
Maintaining weight is important for better prognosis of breast cancer survivors. The associations between weight and cancer-related symptoms are not known. We examined associations among weight, weight change, inflammation, cancer-related symptoms, and health-related quality of life (HRQOL) in a cohort of stage 0-IIIA breast cancer survivors. Participants were recruited on average 6 months (2–12 months) after diagnosis. Height, weight, and C-reactive protein (CRP) were assessed at approximately 30 months post-diagnosis; cancer-related symptoms (chest wall and arm symptoms, vasomotor symptoms, urinary incontinence, vaginal symptoms, cognition/mood problems, sleep, sexual interest/function), and HRQOL (SF-36) were assessed at approximately 40 months post-diagnosis. Weight was measured at baseline in a subset. Data on 661 participants were evaluable for body mass index (BMI); 483 were evaluable for weight change. We assessed associations between BMI (<25.0, 25.0–29.9, ≥30.0 kg/m2), post-diagnosis weight change (lost ≥5 %, weight change <5 %, gained ≥5 %), and CRP (tertile) with cancer-related symptoms and HRQOL using analysis of covariance. Higher symptoms scores indicate more frequent or severe symptoms. Higher HRQOL scores indicate better HRQOL. Compared with those with BMI <25 kg/m2, women with BMI ≥30 kg/m2 had the following scores: increased for arm symptoms (+25.0 %), urinary incontinence (+40.0 %), tendency to nap (+18.9 %), and poorer physical functioning (−15.6 %, all p < 0.05). Obese women had lower scores in trouble falling asleep (−9.9 %; p < 0.05). Compared with weight change <5 %, participants with ≥5 % weight gain had lower scores in physical functioning (−7.2 %), role-physical (−15.5 %) and vitality (−11.2 %), and those with weight loss ≥5 % had lower chest wall (−33.0 %) and arm symptom scores (−35.5 %, all p < 0.05). Increasing CRP tertile was associated with worse scores for chest wall symptoms, urinary incontinence, physical functioning, role-physical, vitality and physical component summary scores (all P trend < 0.05). Future studies should examine whether interventions to maintain a healthy weight and reduce inflammation could alleviate cancer-related symptoms and improve HRQOL.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Meeske K, Smith AW, Alfano CM, McGregor BA, McTiernan A, Baumgartner KB, Malone KE, Reeve BB, Ballard-Barbash R, Bernstein L. Fatigue in breast cancer survivors two to five years post diagnosis: a HEAL Study report. Qual Life Res. 2007;16:947–960. 2007. - PubMed
-
- Gartner R, Jensen MB, Nielsen J, Ewertz M, Kroman N, Kehlet H. Prevalence of and factors associated with persistent pain following breast cancer surgery. JAMA. 2009;302:1985–1992. - PubMed
-
- Mejdahl MK, Andersen KG, Gartner R, Kroman N, Kehlet H. Persistent pain and sensory disturbances after treatment for breast cancer: six year nationwide follow-up study. BMJ. 2013;346:f1865. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

