Gender considerations in ventilatory and metabolic development in rats: special emphasis on the critical period
- PMID: 23797186
- PMCID: PMC3731389
- DOI: 10.1016/j.resp.2013.06.013
Gender considerations in ventilatory and metabolic development in rats: special emphasis on the critical period
Abstract
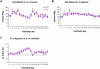
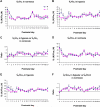
In rats, a critical period exists around postnatal day (P) 12-13, when an imbalance between heightened inhibition and suppressed excitation led to a weakened ventilatory and metabolic response to acute hypoxia. An open question was whether the two genders follow the same or different developmental trends throughout the first 3 postnatal weeks and whether the critical period exists in one or both genders. The present large-scale, in-depth ventilatory and metabolic study was undertaken to address this question. Our data indicated that: (1) the ventilatory and metabolic rates in both normoxia and acute hypoxia were comparable between the two genders from P0 to P21; thus, gender was never significant as a main effect; and (2) the age effect was highly significant in all parameters studies for both genders, and both genders exhibited a significantly weakened response to acute hypoxia during the critical period. Thus, the two genders have comparable developmental trends, and the critical period exists in both genders in rats.
Keywords: Carbon dioxide production; Gender difference; Hypoxia; Oxygen consumption; Respiration.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Postnatal development of metabolic rate during normoxia and acute hypoxia in rats: implication for a sensitive period.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2009 Apr;106(4):1212-22. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.90949.2008. Epub 2008 Dec 31. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2009. PMID: 19118157 Free PMC article.
-
Hering-Breuer reflex in conscious newborn rats: effects of changes in ambient temperature during hypoxia.J Appl Physiol (1985). 1999 Nov;87(5):1656-61. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1999.87.5.1656. J Appl Physiol (1985). 1999. PMID: 10562605
-
Attenuation of the hypoxic ventilatory response in adult rats following one month of perinatal hyperoxia.J Physiol. 1996 Sep 1;495 ( Pt 2)(Pt 2):561-71. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1996.sp021616. J Physiol. 1996. PMID: 8887766 Free PMC article.
-
Implications of hypoxic hypometabolism during mammalian ontogenesis.Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2004 Aug 12;141(3):345-56. doi: 10.1016/j.resp.2004.01.011. Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2004. PMID: 15288604 Review.
-
Developmental plasticity of the hypoxic ventilatory response after perinatal hyperoxia and hypoxia.Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2005 Nov 15;149(1-3):287-99. doi: 10.1016/j.resp.2005.04.003. Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2005. PMID: 16203217 Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanisms underlying a critical period of respiratory development in the rat.Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2019 Jun;264:40-50. doi: 10.1016/j.resp.2019.04.006. Epub 2019 Apr 15. Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2019. PMID: 30999061 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluating the control: minipump implantation and breathing behavior in the neonatal rat.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2016 Sep 1;121(3):615-22. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00080.2016. Epub 2016 Jul 8. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2016. PMID: 27402557 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y. Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J. Roy. Statist. Soc. Ser. B. 1995;57:289–300.
-
- Bertin R, De Marco F, Mouroux I, Portet R. Postnatal development of nonshivering thermogenesis in rats: effects of rearing temperature. J. Dev. Physiol. 1993;19:9–15. - PubMed
-
- Bisgard GE, Olson EB, Jr., Wang ZY, Bavis RW, Fuller DD, Mitchell GS. Adult carotid chemoafferent responses to hypoxia after 1, 2, and 4 wk of postnatal hyperoxia. J. Appl. Physiol. 2003;95:946–952. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

