Including spatial information in nonlinear inversion MR elastography using soft prior regularization
- PMID: 23797239
- PMCID: PMC4107367
- DOI: 10.1109/TMI.2013.2268978
Including spatial information in nonlinear inversion MR elastography using soft prior regularization
Abstract
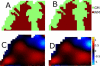
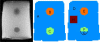
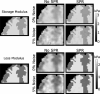
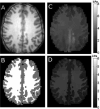
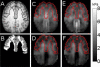
Tissue displacements required for mechanical property reconstruction in magnetic resonance elastography (MRE) are acquired in a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scanner, therefore, anatomical information is available from other imaging sequences. Despite its availability, few attempts to incorporate prior spatial information in the MRE reconstruction process have been reported. This paper implements and evaluates soft prior regularization (SPR), through which homogeneity in predefined spatial regions is enforced by a penalty term in a nonlinear inversion strategy. Phantom experiments and simulations show that when predefined regions are spatially accurate, recovered property values are stable for SPR weighting factors spanning several orders of magnitude, whereas inaccurate segmentation results in bias in the reconstructed properties that can be mitigated through proper choice of regularization weighting. The method was evaluated in vivo by estimating viscoelastic mechanical properties of frontal lobe gray and white matter for five repeated scans of a healthy volunteer. Segmentations of each tissue type were generated using automated software, and statistically significant differences between frontal lobe gray and white matter were found for both the storage modulus and loss modulus . Provided homogeneous property assumptions are reasonable, SPR produces accurate quantitative property estimates for tissue structures which are finer than the resolution currently achievable with fully distributed MRE.
Figures






References
-
- Muthupillai R, Lomas DJ, Rossman PJ, Greenleaf JF, Manduca A, Ehman RL. Magnetic resonance elastography by direct visualization of propagating acoustic strain waves. Science. 1995 Sep.269:1854–1857. - PubMed
-
- Huwart L, et al. Magnetic resonance elastography for the noninvasive staging of liver fibrosis. Gastroenterology. 2008;135(1):32–40. - PubMed
-
- Ehman RL. Science to practice: Can MR elastography be used to detect early steatohepatitis in fatty liver disease. Radiology. 2009;253(1):1. - PubMed
-
- Asbach P, Klatt D, Hamhaber U, Braun J, Somasundaram R, Hamm B, Sack I. Assessment of liver viscoelasticity using multifrequency MR elastography. Magn. Reson. Med. 2008;60(2):373–379. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

