Significant decline in Galactomannan Signal during storage of clinical serum samples
- PMID: 23797658
- PMCID: PMC3742168
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms140712970
Significant decline in Galactomannan Signal during storage of clinical serum samples
Abstract
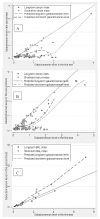
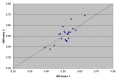
Galactomannan (GM) is widely used for detection of invasive aspergillosis in high-risk haemato-oncology patients. Recent publications have reported a lack of repeatability of GM detection. The objective of this retrospective study was to assess the repeatability of GM levels during storage of clinical samples. In a GM screening strategy, positive sera were repeat tested as per manufacturer's recommendations. Short-term (ST) storage of samples was at +4 °C while long-term (LT) storage was at -80 °C. Bronchoalveolar (BAL) fluid was also repeating tested after ST storage and LT storage. Wilcoxon Signed Ranks Test was employed to assess the repeatability of GM levels. In a subset of 14 GM positive sera, repeat testing was performed on both the original serum and ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) pre-treated sample. There was a significant reduction in GM signals on repeat testing following ST storage (median GM index: 0.65 vs. 0.19; p < 0.001) and LT storage (median GM index: 0.56 vs. 0.10; p < 0.001) of serum samples. Of samples that were initially GM positive, an average GM index reduction of 50% was seen, with approximately two-thirds becoming GM negative on repeat testing of the same sample. In contrast, GM signal loss was not seen on repeat testing of BAL fluid following ST or LT storage. When GM positive serum samples were repeat tested using EDTA pre-treated serum from the first step of the testing protocol, all samples remained GM positive. In contrast, when the same samples were repeat tested from the original collected serum, 9 samples (64%) became GM negative. The significant reduction in GM signals during ST and LT storage of serum samples has implications for clinical management. Although the reasons for GM decline are unknown, they occur prior to the EDTA pre-treatment stage, indicating that the time from phlebotomy to testing should be minimized. BAL fluid GM index values remain stable.
Figures
References
-
- Kuderer N.M., Dale D.C., Crawford J., Cosler L.E., Lyman G.H. Mortality, morbidity, and cost associated with febrile neutropenia in adult cancer patients. Cancer. 2006;106:2258–2266. - PubMed
-
- Wheat L.J., Walsh T.J. Diagnosis of invasive aspergillosis by galactomannan antigenemia detection using an enzyme immunoassay. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2008;27:245–251. - PubMed
-
- Pereira C.N., del Nero G., Lacaz C.S., Machado C.M. The contribution of galactomannan detection in the diagnosis of invasive aspergillosis in bone marrow transplant recipients. Mycopathologia. 2005;159:487–493. - PubMed
-
- Oren I., Avidor I., Sprecher H. Lack of intra-laboratory reproducibility in using Platelia Aspergillus enzyme immunoassay test for detection of Aspergillus galactomannan antigen. Transplant Infect Dis. 2012;14:107–109. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

