Gabapentin or pregabalin for the prophylaxis of episodic migraine in adults
- PMID: 23797675
- PMCID: PMC6599858
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD010609
Gabapentin or pregabalin for the prophylaxis of episodic migraine in adults
Abstract
Background: Some antiepileptic drugs but not others are useful in clinical practice for the prophylaxis of migraine. This might be explained by the variety of actions of these drugs in the central nervous system. The present review is part of an update of a Cochrane review first published in 2004, and previously updated (conclusions not changed) in 2007.
Objectives: To describe and assess the evidence from controlled trials on the efficacy and tolerability of gabapentin/gabapentin enacarbil or pregabalin for preventing migraine attacks in adult patients with episodic migraine.
Search methods: We searched the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL; The Cochrane Library 2012, Issue 12), PubMed/MEDLINE (1966 to 15 January 2013), MEDLINE In-Process (current week, 15 January 2013), and EMBASE (1974 to 15 January 2013) and handsearched Headache and Cephalalgia through January 2013.
Selection criteria: Studies were required to be prospective, controlled trials of gabapentin/gabapentin enacarbil or pregabalin taken regularly to prevent the occurrence of migraine attacks, to improve migraine-related quality of life, or both.
Data collection and analysis: Two review authors independently selected studies and extracted data. For headache frequency data, we calculated mean differences (MDs) between gabapentin and comparator (placebo, active control, or gabapentin in a different dose) for individual studies and pooled these across studies. For dichotomous data on responders (patients with ≥ 50% reduction in headache frequency), we calculated odds ratios (ORs) and numbers needed to treat (NNTs). We also summarised data on adverse events from all single dosage studies and calculated risk differences (RDs) and numbers needed to harm (NNHs).
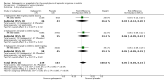
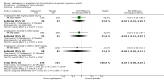
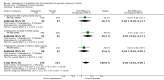
Main results: Five trials on gabapentin and one trial on its prodrug gabapentin enacarbil met the inclusion criteria; no reports on pregabalin were identified. In total, data from 1009 patients were considered. One trial each of gabapentin 900 mg (53 patients), and gabapentin titrated to 1200 mg (63 patients) and 1800 mg (122 patients) failed to show a statistically significant reduction in headache frequency in the active treatment group as compared to the placebo group, whereas one trial of gabapentin titrated to 1800 to 2400 mg (113 patients) demonstrated a small but statistically significant superiority of active treatment for this outcome (MD -0.80; 95% confidence interval (CI) -1.55 to -0.05). The pooled results of these four studies (MD -0.44; 95% CI -1.43 to 0.56; 351 patients) do not demonstrate a significant difference between gabapentin and placebo. One trial of gabapentin titrated to 1800 mg (122 patients) failed to demonstrate a significant difference between active treatment and placebo in the proportion of responders (OR 0.97; 95% CI 0.45 to 2.11), whereas one trial of gabapentin titrated to 1800 to 2400 mg (113 patients) demonstrated a small but statistically significant superiority of active treatment for this outcome (OR 2.79; 95% CI 1.09 to 7.17). The pooled results of these two studies (OR 1.59; 95% CI 0.57 to 4.46; 235 patients) do not demonstrate a significant difference between gabapentin and placebo. Comparisons from one study (135 patients) suggest that gabapentin 2000 mg is no more effective than gabapentin 1200 mg. One trial of gabapentin enacarbil (523 participants) failed to demonstrate a significant difference versus placebo or between doses for gabapentin enacarbil titrated to between 1200 mg and 3000 mg with regard to proportion of responders; there was also no evidence of a dose-response trend. Adverse events, most notably dizziness and somnolence, were common with gabapentin.
Authors' conclusions: The pooled evidence derived from trials of gabapentin suggests that it is not efficacious for the prophylaxis of episodic migraine in adults. Since adverse events were common among the gabapentin-treated patients, it is advocated that gabapentin should not be used in routine clinical practice. Gabapentin enacarbil is not efficacious for the prophylaxis of episodic migraine in adults. There is no published evidence from controlled trials of pregabalin for the prophylaxis of episodic migraine in adults.
Conflict of interest statement
Prof Linde: During the process of preparing this review the author received a travel grant from Allergan in Sweden and was involved as an investigator in a clinical trial in Norway sponsored by AstraZeneca and comparing candesartan, propranolol, and placebo in the prophylaxis of migraine.
Dr Mulleners: The author was a paid consultant for the Merck Dutch Migraine Advisory Board and received a speaker's fee from Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp.
Prof Chronicle: Author deceased. During the process of preparing the original review the author was a paid consultant for Johnson & Johnson and NPS Pharmaceuticals in the USA.
Assoc Prof McCrory: During 2008, the author was a paid expert witness for the plaintiffs in a legal action against the manufacturer of Neurontin (gabapentin). In this capacity, he prepared a systematic review examining previously confidential research reports obtained from the manufacturer (through discovery), along with published trial reports of gabapentin for migraine prophylaxis, and testified at trial.
Figures










References
References to studies included in this review
Di Trapani 2000 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Trapani G, Mei D, Marra C, Mazza S, Capuano A. Gabapentin in the prophylaxis of migraine: a double‐blind randomized placebo‐controlled study. Clinica Terapeutica 2000;151(3):145‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Jimenez 2002 {published data only}
-
- Jimenez‐Hernandez MD, Torrecillas‐Narvaez MD, Friera‐Acebal G. Effectiveness and safety of gabapentin in the preventive treatment of migraine [Eficacia y seguridad de la gabapentina en el tratamiento preventivo de la migrana]. Revista de Neurologia 2002;35(7):603‐6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
RR 4301‐00066 {unpublished data only}
-
- Feuerstein T, Quebe‐Fehling E. A double‐blind, placebo‐controlled, parallel‐group, multicenter study of the safety and efficacy of gabapentin (CI‐945) as a prophylactic interval therapy in patients with common migraine (Protocols 879‐201, ‐205, ‐206, ‐207, ‐209). Research Report No. RR 4301‐00066. Freiburg: Goedecke AG Research and Development; June 25, 1990. Available at: http://dida.library.ucsf.edu/pdf/crr13j10.
RR 995‐00074 {published data only}
-
- Magnus‐Miller L, Bernstein P, Caswell K. Double‐blind, randomized, placebo‐controlled, multicenter trial to determine the efficacy and safety of Neurontin® (gabapentin) in migraine prophylaxis administered in doses divided three times a day (TID) (Protocol 945‐220). Research Report No. RR 995‐00074. Morris Plains, NJ: Parke‐Davis Pharmaceutical Research Division of Warner‐Lambert Company Medical and Scientific Affairs Department; August 24, 1999. Available at: http://dida.library.ucsf.edu/pdf/arr13j10.
RR 995‐00085 {unpublished data only}
-
- Magnus‐Miller L, Bernstein P, Caswell K. Double‐blind, randomized, placebo‐controlled, multicenter trial to determine the efficacy and safety of Neurontin® (gabapentin) in migraine prophylaxis (Protocol 945‐217). Research Report No. RR 995‐00085. Morris Plains, NJ: Parke‐Davis Pharmaceutical Research Division of Warner‐Lambert Company Medical and Scientific Affairs Department; January 20, 2000. Available at: http://dida.library.ucsf.edu/pdf/brr13j10.
Silberstein 2013 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Silberstein S, Goode‐Sellers S, Twomey C, Saiers J, Ascher J. Randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled, phase II trial of gabapentin enacarbil for migraine prophylaxis. Cephalagia 2013;33(2):101‐11. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Cutrer 2001 {published data only}
-
- Cutrer FM. Antiepileptic drugs: how they work in headache. Headache 2001;41 Suppl 1:S3‐S10. - PubMed
Jimenez 1999 {published data only}
-
- Jimenez MD, Freira G, Morales A, Cuartero F, Morralla C, Sol JM, et al. Gabapentine in the prophylaxis of migraine. A pilot study [Gabapentina en la profilaxis de la migrana. Estudio piloto]. Neurologia 1999;14(10):478.
Mathew 2001 {published data only}
-
- Mathew NT, Rapoport A, Saper J, Magnus L, Klapper J, Ramadan N, et al. Efficacy of gabapentin in migraine prophylaxis. Headache 2001;41(2):119‐28. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Merren 1998 {published data only}
-
- Merren MD. Gabapentin for treatment of pain and tremor: a large case series. Southern Medical Journal 1998;91(8):739‐44. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Spira 2003 {published data only}
-
- Spira PJ, Beran RG, Australian Gabapentin Chronic Daily Headache Group. Gabapentin in the prophylaxis of chronic daily headache: a randomized, placebo‐controlled study. Neurology 2003;61(12):1753‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Wessely 1987 {published data only}
-
- Wessely P, Baumgartner C, Klingler D, Kreczi J, Meyerson N, Sailer L, et al. Preliminary results of a double blind study with the new migraine prophylactic drug gabapentin. Cephalalgia 1987;7 Suppl 6:476‐7.
Additional references
Ad Hoc Cttee 1962
-
- Ad Hoc Committee on the Classification of Headache of the National Institute of Neurological Diseases and Blindness. Classification of headache. JAMA 1962;179(9):717‐8.
Alderson 2004
-
- Alderson P, Green S, Higgins JPT, editors. Highly sensitive search strategies for identifying reports of randomized controlled trials in MEDLINE. Cochrane Reviewers' Handbook 4.2.2 [updated December 2003]; Appendix 5b. In: The Cochrane Library, Issue 1, 2004. Chichester, UK: John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Clarke 1996
-
- Clarke CE, MacMillan L, Sondhi S, Wells NE. Economic and social impact of migraine. QJM 1996;89(1):77‐84. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Dalkara 2012
-
- Dalkara S, Karakurt A. Recent progress in anticonvulsant drug research: strategies for anticonvulsant drug development and applications of antiepileptic drugs for non‐epileptic central nervous system disorders. Current Topics in Medicinal Chemistry 2012;12(9):1033‐71. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Drugs.com 2013
-
- Gabapentin User Reviews for Migraine at Drugs.com. http://www.drugs.com/comments/gabapentin/for‐migraine.html (accessed 11 April 2013).
Edmeads 1993
-
- Edmeads J, Findlay H, Tugwell P, Pryse‐Phillips W, Nelson RF, Murray TJ. Impact of migraine and tension‐type headache on life‐style, consulting behaviour, and medication use: a Canadian population survey. Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences 1993;20(2):131‐7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Evers 2009
-
- Evers S, Afra J, Frese A, Goadsby PJ, Linde M, May A, et al. European Federation of Neurological Societies. EFNS guideline on the drug treatment of migraine—revised report of an EFNS task force. European Journal of Neurology 2009;16(9):968‐81. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
GBD 2010 Study
Hollis 1999
ICHD‐II 2004
-
- Headache Classification Subcommittee of the International Headache Society. The International Classification of Headache Disorders: 2nd edition. Cephalalgia 2004;24 Suppl 1:1‐160. - PubMed
IHS Cttee 1988
-
- Headache Classification Committee of the International Headache Society. Classification and diagnostic criteria for headache disorders, cranial neuralgias and facial pain. Cephalalgia 1988;8 Suppl 7:1‐96. - PubMed
Jadad 1996
-
- Jadad AR, Moore RA, Carroll D, Jenkinson C, Reynolds DJ, Gavaghan DJ, et al. Assessing the quality of reports of randomized clinical trials: is blinding necessary?. Controlled Clinical Trials 1996;17(1):1‐12. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Landefeld 2009
-
- Landefeld CS, Steinman MA. The Neurontin legacy —marketing through misinformation and manipulation. New England Journal of Medicine 2009;360(2):103‐6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Linde 2012
-
- Linde M, Gustavsson A, Stovner LJ, Steiner TJ, Barré J, Katsarava Z, et al. The cost of headache disorders in Europe: the Eurolight project. European Journal of Neurology 2012;19(5):703‐11. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Linde 2013a
Linde 2013b
Linde 2013c
Linde 2013d
Mayo Clinic Staff 2011
-
- Mayo Clinic Staff. Migraine: Treatments and drugs. http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/migraine‐headache/DS00120/DSECTION=trea... 2011 June 4 (accessed 11 April 2013).
McCrory 2008
-
- McCrory DC. Report on gabapentin (Neurontin) for migraine prophylaxis: evaluation of efficacy, effectiveness and marketing. Expert consultant’s report. August 11, 2008. Available at: http://dida.library.ucsf.edu/pdf/oxx18q10.
McQuay 1998
-
- McQuay H, Moore R. An Evidence‐based Resource for Pain Relief. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1998.
Mehuys 2012
-
- Mehuys E, Paemeleire K, Hees T, Christiaens T, Bortel LM, Tongelen I, et al. Self‐medication of regular headache: a community pharmacy‐based survey. European Journal of Neurology 2012;19(8):1093‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Olesen 2006
-
- Olesen J, Bousser M‐G, Diener H‐C, Dodick D, First M, Goadsby PJ, et al. Headache Classification Committee. New appendix criteria open for a broader concept of chronic migraine. Cephalalgia 2006;26(6):742‐6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Porter 1992
-
- Porter RJ, Meldrum BS. Antiepileptic drugs. In: Katzung BG editor(s). Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. 5th Edition. Norwalk, CT: Appleton & Lange, 1992:331‐49.
Pringsheim 2012
-
- Pringsheim T, Davenport W, Mackie G, Worthington I, Aubé M, Christie SN, et al. Canadian Headache Society Prophylactic Guidelines Development Group. Canadian Headache Society guideline for migraine prophylaxis. Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences 2012;39(2 Suppl 2):S1‐59. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Saris 2010
-
- U.S.D.J, Saris P. Findings of fact and conclusions of law, In re Neurontin Marketing and Sales Practices Litigation. Civil Action No. 04‐cv‐10739‐PBS, 2010 WL 4325225; 3 November 2010. Available at: http://pacer.mad.uscourts.gov/dc/cgi‐bin/recentops.pl?filename=saris/pdf....
Silberstein 2008
-
- Silberstein S, Saper J, Berenson F, Somogyi M, McCague K, D'Souza J. Oxcarbazepine in migraine headache: a double‐blind, randomized, placebo‐controlled study. Neurology 2008;70(7):548‐55. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Silberstein 2012
-
- Silberstein SD, Holland S, Freitag F, Dodick DW, Argoff C, Ashman E, Quality Standards Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology and the American Headache Society. Evidence‐based guideline update: pharmacologic treatment for episodic migraine prevention in adults: report of the Quality Standards Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology and the American Headache Society. Neurology 2012;78(17):1337‐45. [MEDLINE: ] - PMC - PubMed
Tfelt‐Hansen 2012
-
- Tfelt‐Hansen P, Pascual J, Ramadan N, Dahlöf C, D'Amico D, Diener HC, et al. International Headache Society Clinical Trials Subcommittee. Guidelines for controlled trials of drugs in migraine: third edition. A guide for investigators. Cephalalgia 2012;32(1):6‐38. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Vedula 2009
-
- Vedula SS, Bero L, Scherer RW, Dickersin K. Outcome reporting in industry‐sponsored trials of gabapentin for off‐label use. New England Journal of Medicine 2009;361(20):1963‐71. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Victor 2003
References to other published versions of this review
Chronicle 2004
Mulleners 2008
-
- Mulleners WM, Chronicle EP. Anticonvulsants in migraine prophylaxis: a Cochrane review. Cephalalgia 2008;28(6):585‐97. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

