Optogenetic dissection reveals multiple rhythmogenic modules underlying locomotion
- PMID: 23798384
- PMCID: PMC3710792
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1304365110
Optogenetic dissection reveals multiple rhythmogenic modules underlying locomotion
Abstract
Neural networks in the spinal cord known as central pattern generators produce the sequential activation of muscles needed for locomotion. The overall locomotor network architectures in limbed vertebrates have been much debated, and no consensus exists as to how they are structured. Here, we use optogenetics to dissect the excitatory and inhibitory neuronal populations and probe the organization of the mammalian central pattern generator. We find that locomotor-like rhythmic bursting can be induced unilaterally or independently in flexor or extensor networks. Furthermore, we show that individual flexor motor neuron pools can be recruited into bursting without any activity in other nearby flexor motor neuron pools. Our experiments differentiate among several proposed models for rhythm generation in the vertebrates and show that the basic structure underlying the locomotor network has a distributed organization with many intrinsically rhythmogenic modules.
Keywords: channelrhodopsin-2; halorhodopsin; interneurons; motor neurons.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
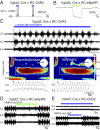

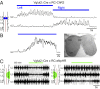

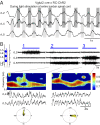

Comment in
-
Network modularity: back to the future in motor control.Curr Biol. 2013 Oct 21;23(20):R936-8. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2013.09.021. Curr Biol. 2013. PMID: 24156817
References
-
- Forssberg H (1985) Ontogeny of human locomotor control. I. Infant stepping, supported locomotion and transition to independent locomotion. Exp Brain Res 57(3):480–493. - PubMed
-
- Kudo N, Nishimaru H. Reorganization of locomotor activity during development in the prenatal rat. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1998;860:306–317. - PubMed
-
- Jordan LM, Liu J, Hedlund PB, Akay T, Pearson KG. Descending command systems for the initiation of locomotion in mammals. Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 2008;57(1):183–191. - PubMed
-
- Lev-Tov A, Etlin A, Blivis D. Sensory-induced activation of pattern generators in the absence of supraspinal control. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010;1198:54–62. - PubMed
-
- Kudo N, Yamada T. N-methyl-D,L-aspartate-induced locomotor activity in a spinal cord-hindlimb muscles preparation of the newborn rat studied in vitro. Neurosci Lett. 1987;75(1):43–48. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

