Adjuvant activity of naturally occurring monophosphoryl lipopolysaccharide preparations from mucosa-associated bacteria
- PMID: 23798540
- PMCID: PMC3754217
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.01150-12
Adjuvant activity of naturally occurring monophosphoryl lipopolysaccharide preparations from mucosa-associated bacteria
Abstract
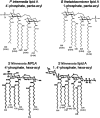
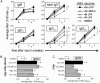
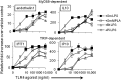
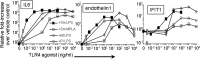
Natural heterogeneity in the structure of the lipid A portion of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) produces differential effects on the innate immune response. Gram-negative bacterial species produce LPS structures that differ from the classic endotoxic LPS structures. These differences include hypoacylation and hypophosphorylation of the diglucosamine backbone, both differences known to decrease LPS toxicity. The effect of decreased toxicity on the adjuvant properties of many of these LPS structures has not been fully explored. Here we demonstrate that two naturally produced forms of monophosphorylated LPS, from the mucosa-associated bacteria Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron and Prevotella intermedia, function as immunological adjuvants for antigen-specific immune responses. Each form of mucosal LPS increased vaccination-initiated antigen-specific antibody titers in both quantity and quality when given simultaneously with vaccine antigen preparations. Interestingly, adjuvant effects on initial T cell clonal expansion were selective for CD4 T cells. No significant increase in CD8 T cell expansion was detected. MyD88/Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) and TRIF/TLR4 signaling pathways showed equally decreased signaling with the LPS forms studied here as with endotoxic LPS or detoxified monophosphorylated lipid A (MPLA). Natural monophosphorylated LPS from mucosa-associated bacteria functions as a weak but effective adjuvant for specific immune responses, with preferential effects on antibody and CD4 T cell responses over CD8 T cell responses.
Figures

References
-
- Vella AT, McCormack JE, Linsley PS, Kappler JW, Marrack P. 1995. Lipopolysaccharide interferes with the induction of peripheral T cell death. Immunity 2:261–270 - PubMed
-
- Skidmore BJ, Chiller JM, Morrison DC, Weigle WO. 1975. Immunologic properties of bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS): correlation between the mitogenic, adjuvant, and immunogenic activities. J. Immunol. 114:770–775 - PubMed
-
- Jacobs DM. 1979. Synergy between T cell-replacing factor and bacterial lipopolysaccharides (LPS) in the primary antibody response in vitro: a model for lipopolysaccharide adjuvant action. J. Immunol. 122:1421–1426 - PubMed
-
- Ribi E. 1984. Beneficial modification of the endotoxin molecule. J. Biol. Response Mod. 3:1–9 - PubMed
-
- Baldrick P, Richardson D, Elliott G, Wheeler AW. 2002. Safety evaluation of monophosphoryl lipid A (MPL): an immunostimulatory adjuvant. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 35:398–413 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

