Ameloblastic fibroma in one-year-old girl
- PMID: 23798857
- PMCID: PMC3687179
- DOI: 10.4103/0973-029X.110734
Ameloblastic fibroma in one-year-old girl
Abstract
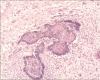
Ameloblastic fibroma (AF) is a relatively rare, slow growing benign mixed odontogenic tumor, comprising of 1.5-4.5% of all odontogenic tumors. It is usually asymptomatic except for the eventual expansion of the jaw. AFs are most common in adolescents and young adults, mostly affecting the mandible as a well-defined uni or multilocular radiolucency. The effective surgical treatment includes enucleation and curettage of the surrounding bone and removal of the affected teeth. Although recurrence of AF is rare, a long term follow up is recommended. This report describes a 1-year-old girl with AF in the mandible and discusses its clinical, radiographic and histological findings.
Keywords: Ameloblastic fibroma; mandible; odontogenic tumour.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




Similar articles
-
Ameloblastic fibroma in a young adult.J Oral Maxillofac Pathol. 2019 Feb;23(Suppl 1):63-65. doi: 10.4103/jomfp.JOMFP_37_16. J Oral Maxillofac Pathol. 2019. PMID: 30967727 Free PMC article.
-
Extensive ameloblastic fibroma in an adolescent patient: a case report with a follow-up of 4 years.Eur J Dent. 2009 Jul;3(3):224-8. Eur J Dent. 2009. PMID: 19756198 Free PMC article.
-
Paediatric oral surgery: endoscopic approach in ameloblastic fibroma management. A preliminary report.Eur J Paediatr Dent. 2018 Dec;19(4):313-316. doi: 10.23804/ejpd.2018.19.04.12. Eur J Paediatr Dent. 2018. PMID: 30567450
-
Ameloblastic fibroma and ameloblastic fibrosarcoma: A systematic review.J Oral Pathol Med. 2018 Apr;47(4):315-325. doi: 10.1111/jop.12622. Epub 2017 Sep 2. J Oral Pathol Med. 2018. PMID: 28776760
-
Ameloblastic Fibro-Odontoma in an Adolescent: A Case Report and Review of Literature.J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2018;42(6):458-460. doi: 10.17796/1053-4625-42.6.10. Epub 2018 Aug 7. J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2018. PMID: 30085878 Review.
Cited by
-
Ameloblastic fibro-odontoma with chondroid tissue formation.Contemp Oncol (Pozn). 2018;22(1):50-53. doi: 10.5114/wo.2018.74395. Epub 2018 Apr 3. Contemp Oncol (Pozn). 2018. PMID: 29692665 Free PMC article.
-
Peripheral Ameloblastic Fibroma: Report of a Rare Case.J Dent (Shiraz). 2016 Dec;17(4):367-369. J Dent (Shiraz). 2016. PMID: 27942554 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kim SG, Jang HS. Ameloblastic fibroma: report of a case. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2002;60:216–8. - PubMed
-
- Chen Y, Wang JM, Li TJ. Ameloblastic fibroma: A review of published studies with special reference to its nature and biological behavior. Oral Oncol. 2007;43:960–9. - PubMed
-
- Mosby EL, Russell D, Noren S, Barker BF. Ameloblastic fibroma in a 7-week-old infant: A case report and review of the literature. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1998;56:368–72. - PubMed
-
- Shafer WG, Hine MK, Levy BM. 5th ed. New Delhi Philadelphia: Elsevier; 2006. A Textbook of Oral Pathology; pp. 400–2.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

