TRPV1 and TRPV4 play pivotal roles in delayed onset muscle soreness
- PMID: 23799042
- PMCID: PMC3684597
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0065751
TRPV1 and TRPV4 play pivotal roles in delayed onset muscle soreness
Abstract
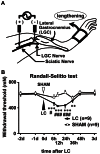
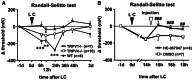
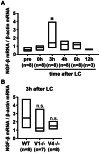
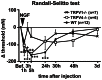
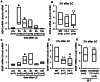
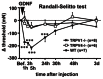
Unaccustomed strenuous exercise that includes lengthening contraction (LC) often causes tenderness and movement related pain after some delay (delayed-onset muscle soreness, DOMS). We previously demonstrated that nerve growth factor (NGF) and glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) are up-regulated in exercised muscle through up-regulation of cyclooxygenase (COX)-2, and they sensitized nociceptors resulting in mechanical hyperalgesia. There is also a study showing that transient receptor potential (TRP) ion channels are involved in DOMS. Here we examined whether and how TRPV1 and/or TRPV4 are involved in DOMS. We firstly evaluated a method to measure the mechanical withdrawal threshold of the deep tissues in wild-type (WT) mice with a modified Randall-Selitto apparatus. WT, TRPV1-/- and TRPV4-/- mice were then subjected to LC. Another group of mice received injection of murine NGF-2.5S or GDNF to the lateral gastrocnemius (LGC) muscle. Before and after these treatments the mechanical withdrawal threshold of LGC was evaluated. The change in expression of NGF, GDNF and COX-2 mRNA in the muscle was examined using real-time RT-PCR. In WT mice, mechanical hyperalgesia was observed 6-24 h after LC and 1-24 h after NGF and GDNF injection. LC induced mechanical hyperalgesia neither in TRPV1-/- nor in TRPV4-/- mice. NGF injection induced mechanical hyperalgesia in WT and TRPV4-/- mice but not in TRPV1-/- mice. GDNF injection induced mechanical hyperalgesia in WT but neither in TRPV1-/- nor in TRPV4-/- mice. Expression of NGF and COX-2 mRNA was significantly increased 3 h after LC in all genotypes. However, GDNF mRNA did not increase in TRPV4-/- mice. These results suggest that TRPV1 contributes to DOMS downstream (possibly at nociceptors) of NGF and GDNF, while TRPV4 is located downstream of GDNF and possibly also in the process of GDNF up-regulation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
EP2 receptor plays pivotal roles in generating mechanical hyperalgesia after lengthening contractions.Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2018 Mar;28(3):826-833. doi: 10.1111/sms.12954. Epub 2017 Aug 11. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2018. PMID: 28759126
-
Upregulated glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor through cyclooxygenase-2 activation in the muscle is required for mechanical hyperalgesia after exercise in rats.J Physiol. 2013 Jun 15;591(12):3035-48. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2012.249235. Epub 2013 Apr 15. J Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23587883 Free PMC article.
-
Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor family members sensitize nociceptors in vitro and produce thermal hyperalgesia in vivo.J Neurosci. 2006 Aug 16;26(33):8588-99. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1726-06.2006. J Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 16914685 Free PMC article.
-
Delayed onset muscle soreness: Involvement of neurotrophic factors.J Physiol Sci. 2016 Jan;66(1):43-52. doi: 10.1007/s12576-015-0397-0. J Physiol Sci. 2016. PMID: 26467448 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Neurotrophin-associated mechanisms of delayed-onset muscle soreness: research progress and perspective].Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2024 Apr 25;76(2):301-308. Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2024. PMID: 38658378 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Neurochemical mechanism of muscular pain: Insight from the study on delayed onset muscle soreness.J Physiol Sci. 2024 Jan 24;74(1):4. doi: 10.1186/s12576-023-00896-y. J Physiol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38267849 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Delayed-Onset Muscle Soreness Begins with a Transient Neural Switch.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Mar 5;26(5):2319. doi: 10.3390/ijms26052319. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40076941 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Delayed-Onset Muscle Soreness Alters Mechanical Sensitivity, but Not Thermal Sensitivity or Pain Modulatory Function.J Pain Res. 2024 Feb 8;17:571-581. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S449787. eCollection 2024. J Pain Res. 2024. PMID: 38347855 Free PMC article.
-
Electrophysiological characteristics of IB4-negative TRPV1-expressing muscle afferent DRG neurons.Biophysics (Nagoya-shi). 2015 Feb 13;11:9-16. doi: 10.2142/biophysics.11.9. eCollection 2015. Biophysics (Nagoya-shi). 2015. PMID: 27493509 Free PMC article.
-
Febrile temperature change modulates CD4 T cell differentiation via a TRPV channel-regulated Notch-dependent pathway.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Sep 8;117(36):22357-22366. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1922683117. Epub 2020 Aug 24. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 32839313 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Armstrong RB (1984) Mechanisms of exercise-induced delayed onset muscular soreness: a brief review. Med Sci Sports Exerc 16: 529–538. - PubMed
-
- Andersen H, Arendt-Nielsen L, Danneskiold-Samsøe B, Graven-Nielsen T (2006) Pressure pain sensitivity and hardness along human normal and sensitized muscle. Somatosens Mot Res 23: 97–109. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

