BMP7 gene transfer via gold nanoparticles into stroma inhibits corneal fibrosis in vivo
- PMID: 23799103
- PMCID: PMC3682981
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0066434
BMP7 gene transfer via gold nanoparticles into stroma inhibits corneal fibrosis in vivo
Abstract
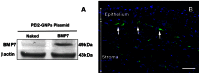
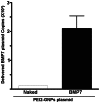
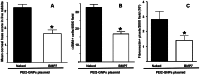
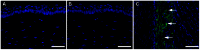
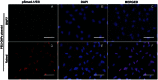
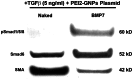
This study examined the effects of BMP7 gene transfer on corneal wound healing and fibrosis inhibition in vivo using a rabbit model. Corneal haze in rabbits was produced with the excimer laser performing -9 diopters photorefractive keratectomy. BMP7 gene was introduced into rabbit keratocytes by polyethylimine-conjugated gold nanoparticles (PEI2-GNPs) transfection solution single 5-minute topical application on the eye. Corneal haze and ocular health in live animals was gauged with stereo- and slit-lamp biomicroscopy. The levels of fibrosis [α-smooth muscle actin (αSMA), F-actin and fibronectin], immune reaction (CD11b and F4/80), keratocyte apoptosis (TUNEL), calcification (alizarin red, vonKossa and osteocalcin), and delivered-BMP7 gene expression in corneal tissues were quantified with immunofluorescence, western blotting and/or real-time PCR. Human corneal fibroblasts (HCF) and in vitro experiments were used to characterize the molecular mechanism mediating BMP7's anti-fibrosis effects. PEI2-GNPs showed substantial BMP7 gene delivery into rabbit keratocytes in vivo (2×10(4) gene copies/ug DNA). Localized BMP7 gene therapy showed a significant corneal haze decrease (1.68±0.31 compared to 3.2±0.43 in control corneas; p<0.05) in Fantes grading scale. Immunostaining and immunoblot analyses detected significantly reduced levels of αSMA (46±5% p<0.001) and fibronectin proteins (48±5% p<0.01). TUNEL, CD11b, and F4/80 assays revealed that BMP7 gene therapy is nonimmunogenic and nontoxic for the cornea. Furthermore, alizarin red, vonKossa and osteocalcin analyses revealed that localized PEI2-GNP-mediated BMP7 gene transfer in rabbit cornea does not cause calcification or osteoblast recruitment. Immunofluorescence of BMP7-transefected HCFs showed significantly increased pSmad-1/5/8 nuclear localization (>88%; p<0.0001), and immunoblotting of BMP7-transefected HCFs grown in the presence of TGFβ demonstrated significantly enhanced pSmad-1/5/8 (95%; p<0.001) and Smad6 (53%, p<0.001), and decreased αSMA (78%; p<0.001) protein levels. These results suggest that localized BMP7 gene delivery in rabbit cornea modulates wound healing and inhibits fibrosis in vivo by counter balancing TGFβ1-mediated profibrotic Smad signaling.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





References
-
- Bedei A, Marabotti A, Giannecchini I, Ferretti C, Montagnani M, et al. (2006) Photorefractive keratectomy in high myopic defects with or without intraoperative mitomycin C: 1-year results. Eur J Ophthalmol 16: 229–234. - PubMed
-
- Camellin M (2004) Laser epithelial keratomileusis with mitomycin C: indications and limits. J Refract Surg 20: S693–S698. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

