Overexpression of RBBP6, alone or combined with mutant TP53, is predictive of poor prognosis in colon cancer
- PMID: 23799110
- PMCID: PMC3684577
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0066524
Overexpression of RBBP6, alone or combined with mutant TP53, is predictive of poor prognosis in colon cancer
Abstract
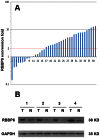
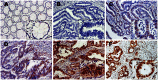
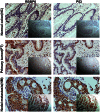
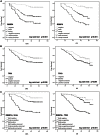
Retinoblastoma binding protein 6 (RBBP6) plays an important role in chaperone-mediated ubiquitination and interacts with TP53 in carcinogenesis. However, the clinicopathologic significance of RBBP6 expression in colon cancer is unknown; in particular, the prognostic value of RBBP6 combined with TP53 expression has not been explored. Therefore, quantitative real-time PCR and western blot analyses were performed to detect RBBP6 expression in colon cancer tissues. RBBP6 and TP53 expression were assessed by immunohistochemistry in a tissue microarray format, in which the primary colon cancer tissue was paired with noncancerous tissue. Tissue specimens were obtained from 203 patients. We found that RBBP6 was overexpressed in colon tumorous tissues and was significantly associated with clinical stage, depth of tumor invasion, lymph node metastasis (LNM), distant metastasis, and histologic grade. Further studies revealed that a corresponding correlation between RBBP6 overexpression and mutant TP53 was evident in colon cancer (r = 0.450; P<0.001). RBBP6 expression was an independent prognostic factor for overall survival (OS) and disease free survival (DFS). Interestingly, patients with tumors that had both RBBP6 overexpression and mutant TP53 protein accumulation relapsed and died within a significantly short period after surgery (P<0.001). Multivariate analysis showed that patients with LNM and patients with both RBBP6- and TP53-positive tumors had extremely poor OS (HR 6.75; 95% CI 2.63-17.35; P<0.001) and DFS (HR 8.08; 95% CI 2.80-23.30; P<0.001). These clinical findings indicate that the assessment of both RBBP6 and mutant TP53 expression will be helpful in predicting colon cancer prognosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- O’Connell JB, Maggard MA, Ko CY (2004) Colon cancer survival rates with the new American Joint Committee on Cancer sixth edition staging. J Natl Cancer Inst 96: 1420–1425. - PubMed
-
- Galandiuk S, Wieand HS, Moertel CG, Cha SS, Fitzgibbons RJ Jr, et al. (1992) Patterns of recurrence after curative resection of carcinoma of the colon and rectum. Surg Gynecol Obstet 174: 27–32. - PubMed
-
- Nakayama KI, Nakayama K (2006) Ubiquitin ligases: cell-cycle control and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 6: 369–381. - PubMed
-
- Pickart CM (2001) Mechanisms underlying ubiquitination. Annu Rev Biochem 70: 503–533. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

