Isolation and characterization of a primary proximal tubular epithelial cell model from human kidney by CD10/CD13 double labeling
- PMID: 23799132
- PMCID: PMC3682988
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0066750
Isolation and characterization of a primary proximal tubular epithelial cell model from human kidney by CD10/CD13 double labeling
Abstract
Renal proximal tubular epithelial cells play a central role in renal physiology and are among the cell types most sensitive to ischemia and xenobiotic nephrotoxicity. In order to investigate the molecular and cellular mechanisms underlying the pathophysiology of kidney injuries, a stable and well-characterized primary culture model of proximal tubular cells is required. An existing model of proximal tubular cells is hampered by the cellular heterogeneity of kidney; a method based on cell sorting for specific markers must therefore be developed. In this study, we present a primary culture model based on the mechanical and enzymatic dissociation of healthy tissue obtained from nephrectomy specimens. Renal epithelial cells were sorted using co-labeling for CD10 and CD13, two renal proximal tubular epithelial markers, by flow cytometry. Their purity, phenotypic stability and functional properties were evaluated over several passages. Our results demonstrate that CD10/CD13 double-positive cells constitute a pure, functional and stable proximal tubular epithelial cell population that displays proximal tubule markers and epithelial characteristics over the long term, whereas cells positive for either CD10 or CD13 alone appear to be heterogeneous. In conclusion, this study describes a method for establishing a robust renal proximal tubular epithelial cell model suitable for further experimentation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
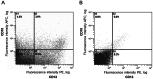


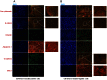
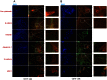

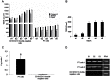
References
-
- Agarwal R (2009) Vitamin D, proteinuria, diabetic nephropathy, and progression of CKD. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 4: 1523–1528. - PubMed
-
- Baer PC, Nockher WA, Haase W, Scherberich JE (1997) Isolation of proximal and distal tubule cells from human kidney by immunomagnetic separation. Technical note. Kidney Int 52: 1321–1331. - PubMed
-
- Weiland C, Ahr HJ, Vohr HW, Ellinger-Ziegelbauer H (2007) Characterization of primary rat proximal tubular cells by gene expression analysis. Toxicol In Vitro 21: 466–491. - PubMed
-
- Brown CD, Sayer R, Windass AS, Haslam IS, De Broe ME, et al. (2008) Characterisation of human tubular cell monolayers as a model of proximal tubular xenobiotic handling. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 233: 428–438. - PubMed
-
- Li W, Choy DF, Lam MS, Morgan T, Sullivan ME, et al. (2003) Use of cultured cells of kidney origin to assess specific cytotoxic effects of nephrotoxins. Toxicol In Vitro 17: 107–113. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

