Vildagliptin is Effective for Glycemic Control in Diabetic Patients Undergoing either Hemodialysis or Peritoneal Dialysis
- PMID: 23801219
- PMCID: PMC3889330
- DOI: 10.1007/s13300-013-0029-8
Vildagliptin is Effective for Glycemic Control in Diabetic Patients Undergoing either Hemodialysis or Peritoneal Dialysis
Abstract
Introduction: Vildagliptin can be used in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and renal impairment. However, there have been few reports investigating the clinical effectiveness of vildagliptin in diabetic patients undergoing hemodialysis. No previous studies have evaluated the use of vildagliptin in patients undergoing peritoneal dialysis. The authors determined the usefulness of vildagliptin for treating type 2 diabetic patients receiving chronic dialysis, including peritoneal dialysis.
Methods: A retrospective study of ten diabetic patients undergoing peritoneal dialysis and five diabetic patients undergoing hemodialysis who were treated with 50 mg/day of vildagliptin was performed. Clinical parameters were investigated for a period of 6 months starting from the vildagliptin therapy.
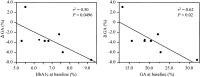
Results: The hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) levels were significantly reduced after baseline in both the peritoneal dialysis and hemodialysis groups, whereas the hemoglobin levels did not change during the follow-up period. The mean change in the HbA1c level (ΔHbA1c) was -0.6 ± 0.9% and -0.5 ± 0.7% among the patients undergoing peritoneal dialysis and hemodialysis, respectively. The glycated albumin (GA) levels were also significantly reduced compared with baseline in the peritoneal dialysis group, although the serum albumin levels did not change. The mean change in the GA level (ΔGA) was -3.4 ± 3.1% and -2.1 ± 2.5% among the patients undergoing peritoneal dialysis and hemodialysis, respectively. Stepwise multivariate analyses demonstrated the level of HbA1c at baseline to be significantly associated with the ΔHbA1c and that the level of GA at baseline was significantly associated with the ΔGA.
Conclusion: Vildagliptin exhibits effectiveness in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus undergoing peritoneal dialysis or hemodialysis. The degree of improvement in the HbA1c and GA levels was dependent on these levels at baseline, similar to the findings of previous reports of subjects without end-stage kidney disease.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Long-term efficacy of vildagliptin in patients with type 2 diabetes undergoing hemodialysis.J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2015 Nov 5;14:83. doi: 10.1186/s40200-015-0214-6. eCollection 2015. J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2015. PMID: 26550558 Free PMC article.
-
Switching from subcutaneous insulin injection to oral vildagliptin administration in hemodialysis patients with type 2 diabetes: a pilot study.Int Urol Nephrol. 2016 Aug;48(8):1349-1355. doi: 10.1007/s11255-016-1305-0. Epub 2016 May 18. Int Urol Nephrol. 2016. PMID: 27193434
-
Rate of the "burnt-out diabetes" phenomenon in patients on peritoneal dialysis.Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2018 Sep;143:254-262. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2018.07.026. Epub 2018 Jul 27. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2018. PMID: 30056189
-
Peritoneal dialysis in diabetic patients.Adv Ren Replace Ther. 2001 Jan;8(1):22-41. doi: 10.1053/jarr.2001.21704. Adv Ren Replace Ther. 2001. PMID: 11172325 Review.
-
Bioimpedance Devices for the Assessment of Body Fluid Volume for Patients Undergoing Dialysis: A Review of the Clinical Effectiveness, Cost-Effectiveness and Guidelines – An Update [Internet].Ottawa (ON): Canadian Agency for Drugs and Technologies in Health; 2015 Aug 25. Ottawa (ON): Canadian Agency for Drugs and Technologies in Health; 2015 Aug 25. PMID: 26985542 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
-
Long-term efficacy of vildagliptin in patients with type 2 diabetes undergoing hemodialysis.J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2015 Nov 5;14:83. doi: 10.1186/s40200-015-0214-6. eCollection 2015. J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2015. PMID: 26550558 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Vildagliptin in the Therapy of Type 2 Diabetic Patients with Renal Dysfunction.Diabetes Ther. 2017 Dec;8(6):1215-1226. doi: 10.1007/s13300-017-0302-3. Epub 2017 Oct 5. Diabetes Ther. 2017. PMID: 28983844 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of diabetes on incidence of peritoneal dialysis-associated peritonitis.PLoS One. 2019 Dec 12;14(12):e0225316. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0225316. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31830041 Free PMC article.
-
Switching from subcutaneous insulin injection to oral vildagliptin administration in hemodialysis patients with type 2 diabetes: a pilot study.Int Urol Nephrol. 2016 Aug;48(8):1349-1355. doi: 10.1007/s11255-016-1305-0. Epub 2016 May 18. Int Urol Nephrol. 2016. PMID: 27193434
-
Diabetes therapies in hemodialysis patients: Dipeptidase-4 inhibitors.World J Diabetes. 2015 Jun 25;6(6):840-9. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v6.i6.840. World J Diabetes. 2015. PMID: 26131325 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

