Perfluorocarbons enhance a T2*-based MRI technique for identifying the penumbra in a rat model of acute ischemic stroke
- PMID: 23801243
- PMCID: PMC3764387
- DOI: 10.1038/jcbfm.2013.86
Perfluorocarbons enhance a T2*-based MRI technique for identifying the penumbra in a rat model of acute ischemic stroke
Abstract
Accurate imaging of ischemic penumbra is crucial for improving the management of acute stroke patients. T2* magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) combined with a T2*oxygen challenge (T2*OC) is being developed to detect penumbra based on changes in blood deoxyhemoglobin. Using 100% O2, T2*OC-defined penumbra exhibits ongoing glucose metabolism and tissue recovery on reperfusion. However, potential limitations in translating this technique include a sinus artefact in human scans with delivery of 100% OC and relatively small signal changes. Here we investigate whether an oxygen-carrying perfluorocarbon (PFC) emulsion can enhance the sensitivity of the technique, enabling penumbra detection with lower levels of inspired oxygen. Stroke was induced in male Sprague-Dawley rats (n=17) with ischemic injury and perfusion deficit determined by diffusion and perfusion MRI, respectively. T2* signal change was measured in regions of interest (ROIs) located within ischemic core, T2*OC-defined penumbra and equivalent contralateral areas during 40% O2±prior PFC injection. Region of interest analyses between groups showed that PFC significantly enhanced the T2* response to 40% O2 in T2*-defined penumbra (mean increase of 10.6±2.3% compared to 5.6±1.5% with 40% O2, P<0.001). This enhancement was specific to the penumbra ROI. Perfluorocarbon emulsions therefore enhances the translational potential of the T2*OC technique for identifying penumbra in acute stroke patients.
Figures
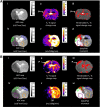


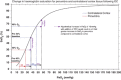
References
-
- The National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke rt-PA Stroke Study Group Tissue plasminogen activator for acute ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med. 1995;333:1581–1587. - PubMed
-
- Furlan M, Marchal G, Viader F, Derlon JM, Baron JC. Spontaneous neurological recovery after stroke and the fate of the ischemic penumbra. Ann Neurol. 1996;40:216–226. - PubMed
-
- Perez A, Restrepo L, Kleinman JT, Barker P, Beauchamp N, Wityk RJ. Patients with diffusion-perfusion mismatch on magnetic resonance imaging 48 hours or more after stroke symptom onset: clinical and imaging features. J Neuroimaging. 2006;16:329–333. - PubMed
-
- Ahmed N, Wahlgren N, Grond M, Hennerici M, Lees KR, Mikulik R, et al. Implementation and outcome of thrombolysis with alteplase 3-4.5 h after an acute stroke: an updated analysis from SITS-ISTR. Lancet Neurol. 2010;9:866–874. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

