Lactosylceramide interacts with and activates cytosolic phospholipase A2α
- PMID: 23801329
- PMCID: PMC3743498
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M113.491431
Lactosylceramide interacts with and activates cytosolic phospholipase A2α
Abstract
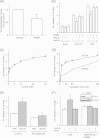
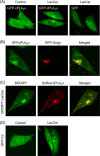
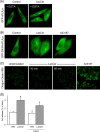
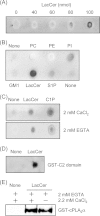
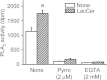
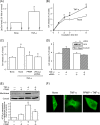
Lactosylceramide (LacCer) is a member of the glycosphingolipid family and is known to be a bioactive lipid in various cell physiological processes. However, the direct targets of LacCer and cellular events mediated by LacCer are largely unknown. In this study, we examined the effect of LacCer on the release of arachidonic acid (AA) and the activity of cytosolic phospholipase A2α (cPLA2α). In CHO-W11A cells, treatment with 1-phenyl-2-palmitoylamino-3-morpholino-1-propanol (PPMP), an inhibitor of glucosylceramide synthase, reduced the glycosphingolipid level, and the release of AA induced by A23187 or platelet-activating factor was inhibited. The addition of LacCer reversed the PPMP effect on the stimulus-induced AA release. Exogenous LacCer stimulated the release of AA, which was decreased by treatment with an inhibitor of cPLA2α or silencing of the enzyme. Treatment of CHO-W11A cells with LacCer induced the translocation of full-length cPLA2α and its C2 domain from the cytosol to the Golgi apparatus. LacCer also induced the translocation of the D43N mutant of cPLA2α. Treatment of L929 cells with TNF-α induced LacCer generation and mediated the translocation of cPLA2α and AA release, which was attenuated by treatment with PPMP. In vitro studies were then conducted to test whether LacCer interacts directly with cPLA2α. Phosphatidylcholine vesicles containing LacCer increased cPLA2α activity. LacCer bound to cPLA2α and its C2 domain in a Ca(2+)-independent manner. Thus, we propose that LacCer is a direct activator of cPLA2α.
Keywords: Arachidonic acid; Glycosphingolipid; Phospholipase A; Sphingolipid; Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Lactosylceramide-Induced Phosphorylation Signaling to Group IVA Phospholipase A2 via Reactive Oxygen Species in Tumor Necrosis Factor-α-Treated Cells.J Cell Biochem. 2017 Dec;118(12):4370-4382. doi: 10.1002/jcb.26091. Epub 2017 May 31. J Cell Biochem. 2017. PMID: 28444900
-
Modulation of the activity of cytosolic phospholipase A2alpha (cPLA2alpha) by cellular sphingolipids and inhibition of cPLA2alpha by sphingomyelin.J Lipid Res. 2010 Apr;51(4):720-8. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M002428. Epub 2009 Oct 16. J Lipid Res. 2010. PMID: 19965591 Free PMC article.
-
Off-target effect of the cPLA2α inhibitor pyrrophenone: Inhibition of calcium release from the endoplasmic reticulum.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016 Oct 7;479(1):61-6. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.09.033. Epub 2016 Sep 9. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016. PMID: 27620490 Free PMC article.
-
Convergence: Lactosylceramide-Centric Signaling Pathways Induce Inflammation, Oxidative Stress, and Other Phenotypic Outcomes.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Feb 12;22(4):1816. doi: 10.3390/ijms22041816. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33673027 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sphingolipids in atherosclerosis and vascular biology.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 1998 Oct;18(10):1523-33. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.18.10.1523. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 1998. PMID: 9763522 Review.
Cited by
-
Metabolic Control of Astrocyte Pathogenic Activity via cPLA2-MAVS.Cell. 2019 Dec 12;179(7):1483-1498.e22. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2019.11.016. Epub 2019 Dec 5. Cell. 2019. PMID: 31813625 Free PMC article.
-
Cytosolic phospholipase A₂: physiological function and role in disease.J Lipid Res. 2015 Aug;56(8):1386-402. doi: 10.1194/jlr.R057588. Epub 2015 Apr 2. J Lipid Res. 2015. PMID: 25838312 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dynamic Role of Phospholipases A2 in Health and Diseases in the Central Nervous System.Cells. 2021 Oct 30;10(11):2963. doi: 10.3390/cells10112963. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34831185 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lactosylceramide promotes hypertrophy through ROS generation and activation of ERK1/2 in cardiomyocytes.Glycobiology. 2014 Jun;24(6):518-31. doi: 10.1093/glycob/cwu020. Epub 2014 Mar 21. Glycobiology. 2014. PMID: 24658420 Free PMC article.
-
Glycolipids implicated as mediators of clinically visible retinal pigment epithelial migration in age-related macular degeneration.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025 Jul 22;122(29):e2503191122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2503191122. Epub 2025 Jul 14. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025. PMID: 40658846 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Murakami M., Taketomi Y., Miki Y., Sato H., Hirabayashi T., Yamamoto K. (2011) Recent progress in phospholipase A2 research: from cells to animals to humans. Prog. Lipid Res. 50, 152–192 - PubMed
-
- Hirabayashi T., Murayama T., Shimizu T. (2004) Regulatory mechanism and physiological role of cytosolic phospholipase A2. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 27, 1168–1173 - PubMed
-
- Evans J. H., Spencer D. M., Zweifach A., Leslie C. C. (2001) Intracellular calcium signals regulating cytosolic phospholipase A2 translocation to internal membranes. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 30150–30160 - PubMed
-
- Tucker D. E., Ghosh M., Ghomashchi F., Loper R., Suram S., John B. S., Girotti M., Bollinger J. G., Gelb M. H., Leslie C. C. (2009) Role of phosphorylation and basic residues in the catalytic domain of cytosolic phospholipase A2α in regulating interfacial kinetics and binding and cellular function. J. Biol. Chem. 284, 9596–9611 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Subramanian P., Vora M., Gentile L. B., Stahelin R. V., Chalfant C. E. (2007) Anionic lipids activate group IVA cytosolic phospholipase A2 via distinct and separate mechanisms. J. Lipid Res. 48, 2701–2708 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

