Virus-associated apoptosis of blood neutrophils as a risk factor for invasive meningococcal disease
- PMID: 23801496
- PMCID: PMC3841771
- DOI: 10.1136/jclinpath-2013-201579
Virus-associated apoptosis of blood neutrophils as a risk factor for invasive meningococcal disease
Abstract
Aims: To quantify a range of haematological indicators of viral infection (leucocyte apoptosis, cytopenia of normal lymphocytes, reactive lymphocyte increase, neutropenia) in patients with recent onset invasive meningococcal disease (IMD), with a view to test the association of viral infection with IMD and identify possible haematological risk factors for its development.
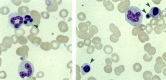
Subjects and methods: 88 patients with recent onset IMD, classified on clinical severity as fatal (n=14), septic shock survived (n=26) and no shock (n=48), and 50 healthy controls were studied. Blood film microscopy and leucocyte counts were used to quantify the virus-associated indicators. Cocci-containing neutrophils were also quantified.
Results: All viral parameters were significantly more frequent or higher in patients than controls, with leucocyte apoptosis found only in the patients. A significant gradient in accord with clinical severity was found for neutrophil and lymphocyte apoptosis, neutropenia and cocci-containing neutrophils. Crucially, apoptotic neutrophils did not contain cocci, and cocci-containing neutrophils were not apoptotic.
Conclusions: The correlation between magnitude of neutrophil apoptosis and severity of IMD suggests a cause-effect relationship. We propose that neutrophil apoptosis is more likely a facilitator rather than an effect of IMD for these reasons: (1) apoptotic neutrophils did not contain cocci and cocci-containing neutrophils were not apoptotic, (2) leucocyte apoptosis is a recognised viral effect and (3) Neisseria meningitidis is incapable of producing a Panton-Valentine type leucocidin. The lymphocyte apoptosis which accompanies neutrophil death may contribute to risk by impairing the generation of microbicidal antibody. Leucocyte apoptosis is a morphological expression of viral immunosuppression and, we suggest, is a likely contributor to a range of viral effects.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Leucocytes; Virus.
Figures



References
-
- Cartwright K, Jones D, Smith A, et al. Influenza A and meningococcal disease. Lancet 1991;338:554–7 - PubMed
-
- Moore P, Hierholzer J, DeWitt W, et al. Respiratory viruses and mycoplasma as cofactors for epidemic group A meningococcal meningitis. JAMA 1990;264:1271–5 - PubMed
-
- McCall B, Neill A, Young M. Risk factors for invasive meningococcal disease in southern Queensland 2000–2001. Internal Med J 2004;34:464–68 - PubMed
-
- Coen P, Tully J, Stuart J, et al. Is it exposure to cigarette smoke or to smokers which increases the risk of meningococcal disease in teenagers? Int J Epidemiol 2006;35:330–6 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
