Alloantibodies to a paternally derived RBC KEL antigen lead to hemolytic disease of the fetus/newborn in a murine model
- PMID: 23801629
- PMCID: PMC3750342
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2013-03-488874
Alloantibodies to a paternally derived RBC KEL antigen lead to hemolytic disease of the fetus/newborn in a murine model
Abstract
Exposure to nonself red blood cell (RBC) antigens, either from transfusion or pregnancy, may result in alloimmunization and incompatible RBC clearance. First described as a pregnancy complication 80 years ago, hemolytic disease of the fetus and newborn (HDFN) is caused by alloimmunization to paternally derived RBC antigens. Despite the morbidity/mortality of HDFN, women at risk for RBC alloimmunization have few therapeutic options. Given that alloantibodies to antigens in the KEL family are among the most clinically significant, we developed a murine model with RBC-specific expression of the human KEL antigen to evaluate the impact of maternal/fetal KEL incompatibility. After exposure to fetal KEL RBCs during successive pregnancies with KEL-positive males, 21 of 21 wild-type female mice developed anti-KEL alloantibodies; intrauterine fetal anemia and/or demise occurred in a subset of KEL-positive pups born to wild type, but not agammaglobulinemic mothers. Similar to previous observations in humans, pregnancy-associated alloantibodies were detrimental in a transfusion setting, and transfusion-associated alloantibodies were detrimental in a pregnancy setting. This is the first pregnancy-associated HDFN model described to date, which will serve as a platform to develop targeted therapies to prevent and/or mitigate the dangers of RBC alloantibodies to fetuses and newborns.
Figures

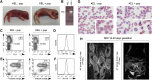
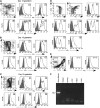
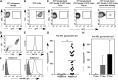
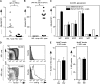

Comment in
-
A mouse model of hemolytic disease of the newborn.Blood. 2013 Aug 22;122(8):1334-5. doi: 10.1182/blood-2013-07-512715. Blood. 2013. PMID: 23970354
References
-
- Reid ME, Mohandas N. Red blood cell blood group antigens: structure and function. Semin Hematol. 2004;41(2):93–117. - PubMed
-
- Reid ME, Lomas-Francis C. The Blood Group Antigen Facts Book. 2nd ed. Amsterdam: Elsevier Academic Press; 2004.
-
- Moise KJ., Jr Management of rhesus alloimmunization in pregnancy. Obstet Gynecol. 2002;100(3):600–611. - PubMed
-
- Moise KJ. Fetal anemia due to non-Rhesus-D red-cell alloimmunization. Semin Fetal Neonatal Med. 2008;13(4):207–214. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

