Red blood cell microparticles: clinical relevance
- PMID: 23801926
- PMCID: PMC3678264
- DOI: 10.1159/000342228
Red blood cell microparticles: clinical relevance
Abstract
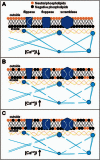
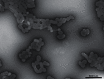
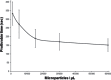
Microparticles are small phospholipid vesicles of less than 1 µm released into the blood flow by various types of cells such as endothelial, platelet, white or red blood cells. They are involved in many biological and physiological processes including hemostasis. In addition, an elevated number of microparticles in the blood is observed in various pathological situations. In the context of transfusion, erythrocyte-derived microparticles are found in red blood cell concentrates. Their role is not elucidated, and they are considered as a type of storage lesion. The purpose of this review is to present recent data showing that erythrocyte-derived microparticles most likely play a role in transfusion medicine and could cause transfusion complications.
Mikropartikel sind kleine (<1 μm) Phospholipid-Vesikel, die von verschiedenartigen Zellen wie Endothelzellen, Thrombozyten sowie weißen und roten Blutkörperchen in den Blutstrom entlassen werden. Sie sind an vielen biologischen und physiologischen Prozessen einschließlich der Hämostase beteiligt. Des Weiteren wird eine erhöhte Anzahl an Mikropartikeln im Blut in verschiedenen pathologischen Situationen beobachtet. Im Zusammenhang mit Transfusionen sind von Erythrozyten abstammende Mikropartikel in Erythrozytenkonzentraten anzutreffen. Ihre Rolle ist ungeklärt, und sie werden als Lagerungsschaden betrachtet. Ziel dieser Übersichtsarbeit ist die Präsentation jüngster Daten, die zeigen, dass von Erythrozyten stammende Mikropartikel höchstwahrscheinlich eine Rolle in der Transfusionsmedizin spielen und zu Komplikationen führen können.
Keywords: Ageing; Microparticles; Red blood cell concentrates; Red blood cells; Transfusion.
Figures
References
-
- Diamant M, Tushuizen ME, Sturk A, Nieuwland R. Cellular microparticles: new players in the field of vascular disease? Eur J Clin Invest. 2004;34:392–401. - PubMed
-
- Simak J, Gelderman MP. Cell membrane microparticles in blood and blood products: potentially pathogenic agents and diagnostic markers. Transfus Med Rev. 2006;20:1–26. - PubMed
-
- Morel O, Toti F, Hugel B, Bakouboula B, Camoin-Jau L, Dignat-George F, Freyssinet JM. Procoagulant microparticles – disrupting the vascular homeostasis equation? Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2006;26:2594–2604. - PubMed
-
- Hugel B, Carmen M, Martinez MC, Kunzelmann C, Freyssinet JM. Membrane microparticles: two sides of the coin. Physiology. 2005;20:22–27. - PubMed
-
- An XL, Guo XH, Sum H, Morrow J, Gratzer W, Mohandas N. Phosphatidylserine binding sites in erythroid spectrin: location and implications for membrane stability. Biochemistry. 2004;43:310–315. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

