Comparative feedstock analysis in Setaria viridis L. as a model for C4 bioenergy grasses and Panicoid crop species
- PMID: 23802002
- PMCID: PMC3685855
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2013.00181
Comparative feedstock analysis in Setaria viridis L. as a model for C4 bioenergy grasses and Panicoid crop species
Abstract
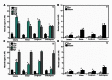
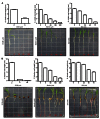
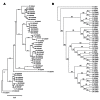
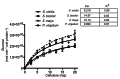
Second generation feedstocks for bioethanol will likely include a sizable proportion of perennial C4 grasses, principally in the Panicoideae clade. The Panicoideae contain agronomically important annual grasses including Zea mays L. (maize), Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench (sorghum), and Saccharum officinarum L. (sugar cane) as well as promising second generation perennial feedstocks including Miscanthus×giganteus and Panicum virgatum L. (switchgrass). The underlying complexity of these polyploid grass genomes is a major limitation for their direct manipulation and thus driving a need for rapidly cycling comparative model. Setaria viridis (green millet) is a rapid cycling C4 panicoid grass with a relatively small and sequenced diploid genome and abundant seed production. Stable, transient, and protoplast transformation technologies have also been developed for Setaria viridis making it a potentially excellent model for other C4 bioenergy grasses. Here, the lignocellulosic feedstock composition, cellulose biosynthesis inhibitor response and saccharification dynamics of Setaria viridis are compared with the annual sorghum and maize and the perennial switchgrass bioenergy crops as a baseline study into the applicability for translational research. A genome-wide systematic investigation of the cellulose synthase-A genes was performed identifying eight candidate sequences. Two developmental stages; (a) metabolically active young tissue and (b) metabolically plateaued (mature) material are examined to compare biomass performance metrics.
Keywords: Panicoideae; Setaria; biofuel; cell wall; cellulose synthase; lignocellulose.
Figures



References
-
- Alonso M. D., Wettstein S. G., Mellmer M. A., Gurbuz E. I., Dumesic J. A. (2013) Integrated conversion of hemicellulose and cellulose from lignocellulosic biomass. Energy Environ. Sci. 6 76–8010.1039/c2ee23617f - DOI
-
- Andersson S., Serimaa R., Paakkari T., Saranpää P., Pesonen E. (2003) Crystallinity of wood and the size of cellulose crystallites in Norway spruce (Picea abies). J. Wood Sci. 49 531–53710.1007/s10086-003-0518-x - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

