BRCA1 in the DNA damage response and at telomeres
- PMID: 23802008
- PMCID: PMC3689208
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2013.00085
BRCA1 in the DNA damage response and at telomeres
Abstract
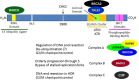
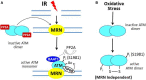
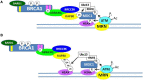
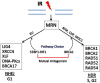
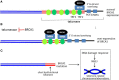
Mutations of the breast and ovarian cancer susceptibility gene 1 (BRCA1) account for about 40-45% of hereditary breast cancer cases. Moreover, a significant fraction of sporadic (non-hereditary) breast and ovarian cancers exhibit reduced or absent expression of the BRCA1 protein, suggesting an additional role for BRCA1 in sporadic cancers. BRCA1 follows the classic pattern of a highly penetrant Knudsen-type tumor suppressor gene in which one allele is inactivated through a germ-line mutation and the other is mutated or deleted within the tumor. BRCA1 is a multi-functional protein but it is not fully understood which function(s) is (are) most important for tumor suppression, nor is it clear why BRCA1-mutations confer a high risk for breast and ovarian cancers and not a broad spectrum of tumor types. Here, we will review BRCA1 functions in the DNA damage response (DDR), which are likely to contribute to tumor suppression. In the process, we will highlight some of the controversies and unresolved issues in the field. We will also describe a recently identified and under-investigated role for BRCA1 in the regulation of telomeres and the implications of this role in the DDR and cancer suppression.
Keywords: DNA damage response; DNA damage signaling; ataxia-telangiectasia mutated; base excision repair; breast cancer susceptibility gene 1; homology-directed repair; telomeres.
Figures
Similar articles
-
BRCA1 gene in breast cancer.J Cell Physiol. 2003 Jul;196(1):19-41. doi: 10.1002/jcp.10257. J Cell Physiol. 2003. PMID: 12767038 Review.
-
Differing effects of breast cancer 1, early onset (BRCA1) and ataxia-telangiectasia mutated (ATM) mutations on cellular responses to ionizing radiation.Int J Radiat Biol. 2003 Oct;79(10):817-29. doi: 10.1080/09553000310001610952. Int J Radiat Biol. 2003. PMID: 14630541
-
Ovarian Cancer Gene Therapy with BRCA1-An Overview.Methods Mol Med. 2000;35:593-607. doi: 10.1385/1-59259-086-1:593. Methods Mol Med. 2000. PMID: 21390833
-
A multi-gene panel study in hereditary breast and ovarian cancer in Colombia.Fam Cancer. 2018 Jan;17(1):23-30. doi: 10.1007/s10689-017-0004-z. Fam Cancer. 2018. PMID: 28528518
-
BRCA1 in non-inherited breast carcinomas (Review).Oncol Rep. 2002 Nov-Dec;9(6):1329-33. Oncol Rep. 2002. PMID: 12375043 Review.
Cited by
-
BRCA1-BARD1 regulates transcription through BRD4 in Xenopus nucleoplasmic extract.Nucleic Acids Res. 2021 Apr 6;49(6):3263-3273. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkab111. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021. PMID: 33660782 Free PMC article.
-
Strong preference of BRCA1 protein to topologically constrained non-B DNA structures.BMC Mol Biol. 2016 Jun 8;17(1):14. doi: 10.1186/s12867-016-0068-6. BMC Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 27277344 Free PMC article.
-
Chemotherapeutic compounds targeting the DNA double-strand break repair pathways: the good, the bad, and the promising.Front Oncol. 2014 Apr 22;4:86. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2014.00086. eCollection 2014. Front Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24795863 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Arabidopsis RETINOBLASTOMA RELATED directly regulates DNA damage responses through functions beyond cell cycle control.EMBO J. 2017 May 2;36(9):1261-1278. doi: 10.15252/embj.201694561. Epub 2017 Mar 20. EMBO J. 2017. PMID: 28320736 Free PMC article.
-
BRCA-related ATM-mediated DNA double-strand break repair and ovarian aging.Hum Reprod Update. 2020 Jan 1;26(1):43-57. doi: 10.1093/humupd/dmz043. Hum Reprod Update. 2020. PMID: 31822904 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

