Atrial fibrillation in obstructive sleep apnea
- PMID: 23802045
- PMCID: PMC3691496
- DOI: 10.4330/wjc.v5.i6.157
Atrial fibrillation in obstructive sleep apnea
Abstract
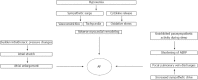
Atrial fibrillation (AF) is a common arrhythmia with rising incidence. Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is prevalent among patients with AF. This observation has prompted significant research in understanding the relationship between OSA and AF. Multiple studies support a role of OSA in the initiation and progression of AF. This association has been independent of obesity, body mass index and hypertension. Instability of autonomic tone and wide swings in intrathoracic pressure are seen in OSA. These have been mechanistically linked to initiation of AF in OSA patients by lowering atrial effective refractory period, promoting pulmonary vein discharges and atrial dilation. OSA not only promotes initiation of AF but also makes management of AF difficult. Drug therapy and electrical cardioversion for AF are less successful in presence of OSA. There has been higher rate of early and overall recurrence after catheter ablation of AF in patients with OSA. Treatment of OSA with continuous positive airway pressure has been shown to improve control of AF. However, additional studies are needed to establish a stronger relationship between OSA treatment and success of AF therapies. There should be heightened suspicion of OSA in patients with AF. There is a need for guidelines to screen for OSA as a part of AF management.
Keywords: Ablation; Anti-arrhythmic medications; Atrial fibrillation; Cardioversion; Obstructive sleep apnea.
Figures
References
-
- Braunwald E. Shattuck lecture--cardiovascular medicine at the turn of the millennium: triumphs, concerns, and opportunities. N Engl J Med. 1997;337:1360–1369. - PubMed
-
- Wolf PA, Benjamin EJ, Belanger AJ, Kannel WB, Levy D, D’Agostino RB. Secular trends in the prevalence of atrial fibrillation: The Framingham Study. Am Heart J. 1996;131:790–795. - PubMed
-
- Calkins H, Brugada J, Packer DL, Cappato R, Chen SA, Crijns HJ, Damiano RJ, Davies DW, Haines DE, Haissaguerre M, et al. HRS/EHRA/ECAS expert consensus statement on catheter and surgical ablation of atrial fibrillation: recommendations for personnel, policy, procedures and follow-up. A report of the Heart Rhythm Society (HRS) Task Force on Catheter and Surgical Ablation of Atrial Fibrillation developed in partnership with the European Heart Rhythm Association (EHRA) and the European Cardiac Arrhythmia Society (ECAS); in collaboration with the American College of Cardiology (ACC), American Heart Association (AHA), and the Society of Thoracic Surgeons (STS). Endorsed and approved by the governing bodies of the American College of Cardiology, the American Heart Association, the European Cardiac Arrhythmia Society, the European Heart Rhythm Association, the Society of Thoracic Surgeons, and the Heart Rhythm Society. Europace. 2007;9:335–379. - PubMed
-
- Gami AS, Pressman G, Caples SM, Kanagala R, Gard JJ, Davison DE, Malouf JF, Ammash NM, Friedman PA, Somers VK. Association of atrial fibrillation and obstructive sleep apnea. Circulation. 2004;110:364–367. - PubMed
-
- Braga B, Poyares D, Cintra F, Guilleminault C, Cirenza C, Horbach S, Macedo D, Silva R, Tufik S, De Paola AA. Sleep-disordered breathing and chronic atrial fibrillation. Sleep Med. 2009;10:212–216. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources