Inter-residue coupling contributes to high-affinity subtype-selective binding of α-bungarotoxin to nicotinic receptors
- PMID: 23802200
- PMCID: PMC3912756
- DOI: 10.1042/BJ20130638
Inter-residue coupling contributes to high-affinity subtype-selective binding of α-bungarotoxin to nicotinic receptors
Abstract
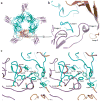
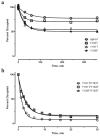
The crystal structure of a pentameric α7 ligand-binding domain chimaera with bound α-btx (α-bungarotoxin) showed that of the five conserved aromatic residues in α7, only Tyr¹⁸⁴ in loop C of the ligand-binding site was required for high-affinity binding. To determine whether the contribution of Tyr¹⁸⁴ depends on local residues, we generated mutations in an α7/5HT(3A) (5-hydroxytryptamine type 3A) receptor chimaera, individually and in pairs, and measured ¹²⁵I-labelled α-btx binding. The results show that mutations of individual residues near Tyr¹⁸⁴ do not affect α-btx affinity, but pairwise mutations decrease affinity in an energetically coupled manner. Kinetic measurements show that the affinity decreases arise through increases in the α-btx dissociation rate with little change in the association rate. Replacing loop C in α7 with loop C from the α-btx-insensitive α2 or α3 subunits abolishes high-affinity α-btx binding, but preserves acetylcholine-elicited single channel currents. However, in both the α2 and α3 construct, mutating either residue that flanks Tyr¹⁸⁴ to its α7 counterpart restores high-affinity α-btx binding. Analogously, in α7, mutating both residues that flank Tyr¹⁸⁴ to the α2 or α3 counterparts abolishes high-affinity α-btx binding. Thus interaction between Tyr¹⁸⁴ and local residues contributes to high-affinity subtype-selective α-btx binding.
Figures




References
-
- Chang CC, Lee CY. Isolation of neurotoxins from the venom of Bungaris multicinctus and their modes of neuromuscular blocking action. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1963;144:241–257. - PubMed
-
- Lee CY. Chemistry and pharmacology of polypeptide toxins in snake venoms. Annu Rev Pharmacol. 1972;12:265–286. - PubMed
-
- Weber M, Changeux JP. Binding of Naja nicricollis (3H) α-toxin to membrane fragments from Electropherus and Torpedo electric organs. I Binding of the tritiated α-neurotoxin in the absence of effector. Mol Pharmacol. 1974;10:1–14. - PubMed
-
- Weiland G, Georgia B, Wee VT, Chignell CF, Taylor P. Ligand interactions with cholinergic receptor-enriched membranes from Torpedo: influence of agonist exposure on receptor properties. Mol Pharmacol. 1976;12:1091–1105. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

