Targeted inhibition of VEGF receptor 2: an update on ramucirumab
- PMID: 23803182
- PMCID: PMC4131847
- DOI: 10.1517/14712598.2013.810717
Targeted inhibition of VEGF receptor 2: an update on ramucirumab
Abstract
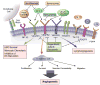
Introduction: Ramucirumab (IMC-1121B) is a fully humanized IgG1 monoclonal antibody, targeting the extracellular domain of VEGF receptor 2 (VEGFR2). Numerous Phase I - II trials in various malignancies have shown promising clinical antitumor efficacy and tolerability. Most recently, the large Phase III REGARD trial evaluated ramucirumab in patients with refractory metastatic gastric cancer. Patients receiving ramucirumab experienced a median overall survival of 5.2 months compared to 3.8 months on placebo.
Areas covered: The purpose of this article is to review the preclinical motivation for VEGFR2-targeted therapies and survey recent data from clinical trials involving ramucirumab, as well as highlight ongoing studies.
Expert opinion: Rational multi-target approaches to angiogenesis are needed to overcome resistance mechanisms. Predictive angiogenic biomarkers are also needed to optimize patient selection for novel anti-angiogenic agents.
Figures
References
-
- Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. The hallmarks of cancer. Cell. 2000 Jan 7;100(1):57–70. - PubMed
-
- Hurwitz H, Fehrenbacher L, Novotny W, Cartwright T, Hainsworth J, Heim W, et al. Bevacizumab plus irinotecan, fluorouracil, and leucovorin for metastatic colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med. 2004 Jun 3;350(23):2335–42. - PubMed
-
- Sandler A, Gray R, Perry MC, Brahmer J, Schiller JH, Dowlati A, et al. Paclitaxel-carboplatin alone or with bevacizumab for non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2006 Dec 14;355(24):2542–50. - PubMed
-
- Motzer RJ, Hutson TE, Tomczak P, Michaelson MD, Bukowski RM, Rixe O, et al. Sunitinib versus interferon alfa in metastatic renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2007 Jan 11;356(2):115–24. - PubMed
-
- Llovet JM, Ricci S, Mazzaferro V, Hilgard P, Gane E, Blanc JF, et al. Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2008 Jul 24;359(4):378–90. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
